Correct model card
Browse files
README.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,88 +1,42 @@
|
|
| 1 |
---
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
license: apache-2.0
|
| 3 |
-
license_link: https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen3-4B
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
base_model:
|
| 5 |
-
- Qwen/Qwen3-4B
|
| 6 |
-
tags:
|
| 7 |
-
- qwen
|
| 8 |
-
- qwen3
|
| 9 |
-
- transformers
|
| 10 |
---
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
-
# Qwen3-4B
|
| 13 |
<a href="https://chat.qwen.ai/" target="_blank" style="margin: 2px;">
|
| 14 |
<img alt="Chat" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%92%9C%EF%B8%8F%20Qwen%20Chat%20-536af5" style="display: inline-block; vertical-align: middle;"/>
|
| 15 |
</a>
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
-
## Highlights
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
-
- **
|
| 22 |
-
- **
|
| 23 |
-
- **
|
| 24 |
-
|
| 25 |
-
**
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
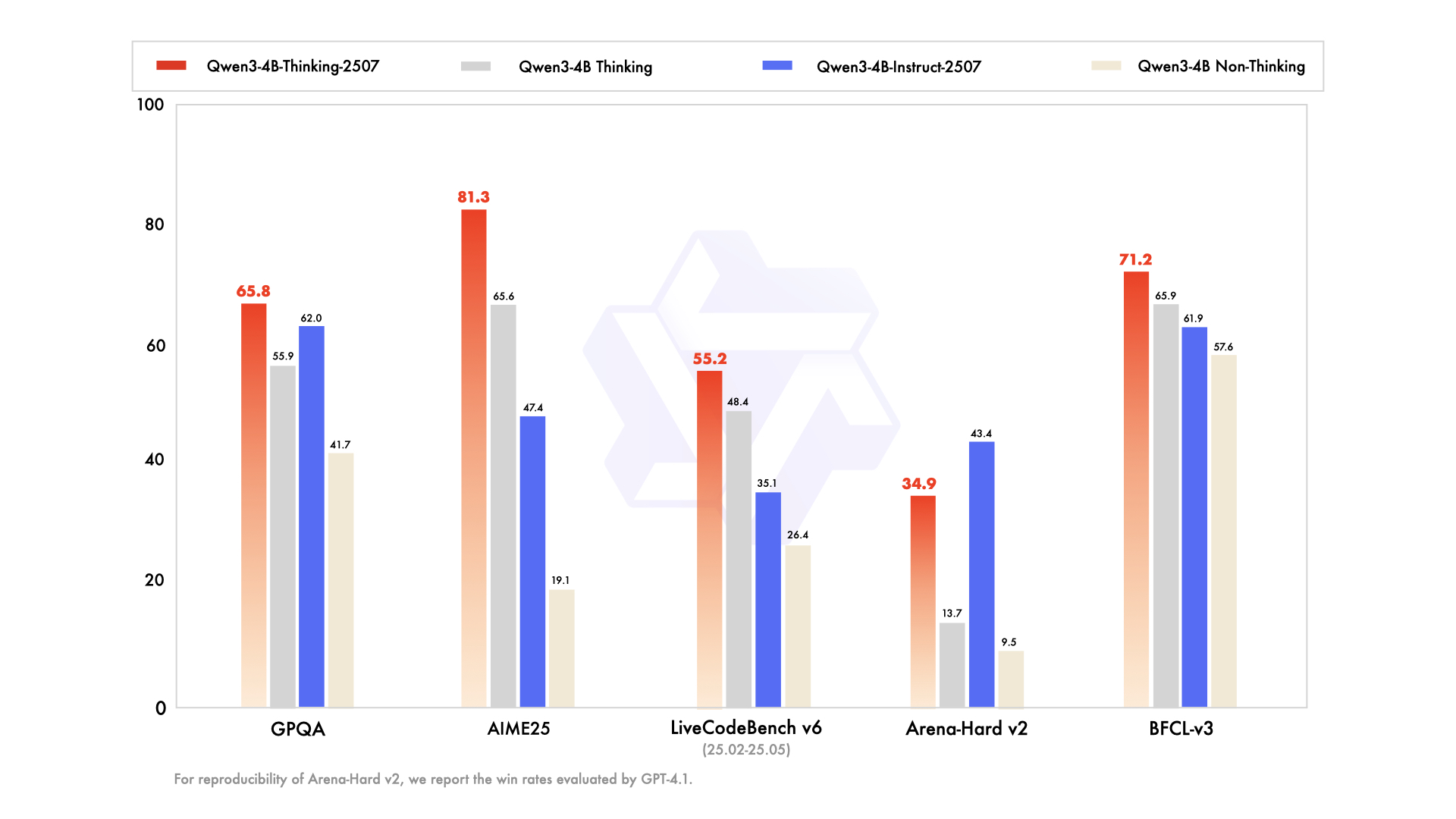
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
## Model Overview
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
-
**Qwen3-4B
|
| 32 |
- Type: Causal Language Models
|
| 33 |
- Training Stage: Pretraining & Post-training
|
| 34 |
- Number of Parameters: 4.0B
|
| 35 |
- Number of Paramaters (Non-Embedding): 3.6B
|
| 36 |
- Number of Layers: 36
|
| 37 |
- Number of Attention Heads (GQA): 32 for Q and 8 for KV
|
| 38 |
-
- Context Length:
|
| 39 |
-
|
| 40 |
-
**NOTE: This model supports only thinking mode. Meanwhile, specifying `enable_thinking=True` is no longer required.**
|
| 41 |
-
|
| 42 |
-
Additionally, to enforce model thinking, the default chat template automatically includes `<think>`. Therefore, it is normal for the model's output to contain only `</think>` without an explicit opening `<think>` tag.
|
| 43 |
|
| 44 |
For more details, including benchmark evaluation, hardware requirements, and inference performance, please refer to our [blog](https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/qwen3/), [GitHub](https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3), and [Documentation](https://qwen.readthedocs.io/en/latest/).
|
| 45 |
|
| 46 |
-
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
|
| 49 |
-
|
| 50 |
-
| | Qwen3-30B-A3B Thinking | Qwen3-4B Thinking | Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507 |
|
| 51 |
-
|--- | --- | --- | --- |
|
| 52 |
-
| **Knowledge** | | |
|
| 53 |
-
| MMLU-Pro | **78.5** | 70.4 | 74.0 |
|
| 54 |
-
| MMLU-Redux | **89.5** | 83.7 | 86.1 |
|
| 55 |
-
| GPQA | **65.8** | 55.9 | **65.8** |
|
| 56 |
-
| SuperGPQA | **51.8** | 42.7 | 47.8 |
|
| 57 |
-
| **Reasoning** | | |
|
| 58 |
-
| AIME25 | 70.9 | 65.6 | **81.3** |
|
| 59 |
-
| HMMT25 | 49.8 | 42.1 | **55.5** |
|
| 60 |
-
| LiveBench 20241125 | **74.3** | 63.6 | 71.8 |
|
| 61 |
-
| **Coding** | | |
|
| 62 |
-
| LiveCodeBench v6 (25.02-25.05) | **57.4** | 48.4 | 55.2 |
|
| 63 |
-
| CFEval | **1940** | 1671 | 1852 |
|
| 64 |
-
| OJBench | **20.7** | 16.1 | 17.9 |
|
| 65 |
-
| **Alignment** | | |
|
| 66 |
-
| IFEval | 86.5 | 81.9 | **87.4** |
|
| 67 |
-
| Arena-Hard v2$ | **36.3** | 13.7 | 34.9 |
|
| 68 |
-
| Creative Writing v3 | **79.1** | 61.1 | 75.6 |
|
| 69 |
-
| WritingBench | 77.0 | 73.5 | **83.3** |
|
| 70 |
-
| **Agent** | | |
|
| 71 |
-
| BFCL-v3 | 69.1 | 65.9 | **71.2** |
|
| 72 |
-
| TAU1-Retail | 61.7 | 33.9 | **66.1** |
|
| 73 |
-
| TAU1-Airline | 32.0 | 32.0 | **48.0** |
|
| 74 |
-
| TAU2-Retail | 34.2 | 38.6 | **53.5** |
|
| 75 |
-
| TAU2-Airline | 36.0 | 28.0 | **58.0** |
|
| 76 |
-
| TAU2-Telecom | 22.8 | 17.5 | **27.2** |
|
| 77 |
-
| **Multilingualism** | | |
|
| 78 |
-
| MultiIF | 72.2 | 66.3 | **77.3** |
|
| 79 |
-
| MMLU-ProX | **73.1** | 61.0 | 64.2 |
|
| 80 |
-
| INCLUDE | **71.9** | 61.8 | 64.4 |
|
| 81 |
-
| PolyMATH | 46.1 | 40.0 | **46.2** |
|
| 82 |
-
|
| 83 |
-
$ For reproducibility, we report the win rates evaluated by GPT-4.1.
|
| 84 |
-
|
| 85 |
-
\& For highly challenging tasks (including PolyMATH and all reasoning and coding tasks), we use an output length of 81,920 tokens. For all other tasks, we set the output length to 32,768.
|
| 86 |
|
| 87 |
## Quickstart
|
| 88 |
|
|
@@ -97,7 +51,7 @@ The following contains a code snippet illustrating how to use the model generate
|
|
| 97 |
```python
|
| 98 |
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
| 99 |
|
| 100 |
-
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen3-4B
|
| 101 |
|
| 102 |
# load the tokenizer and the model
|
| 103 |
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
|
@@ -116,6 +70,7 @@ text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
|
|
| 116 |
messages,
|
| 117 |
tokenize=False,
|
| 118 |
add_generation_prompt=True,
|
|
|
|
| 119 |
)
|
| 120 |
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
|
| 121 |
|
|
@@ -136,25 +91,128 @@ except ValueError:
|
|
| 136 |
thinking_content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[:index], skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
|
| 137 |
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[index:], skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
|
| 138 |
|
| 139 |
-
print("thinking content:", thinking_content)
|
| 140 |
print("content:", content)
|
| 141 |
-
|
| 142 |
```
|
| 143 |
|
| 144 |
For deployment, you can use `sglang>=0.4.6.post1` or `vllm>=0.8.5` or to create an OpenAI-compatible API endpoint:
|
| 145 |
- SGLang:
|
| 146 |
```shell
|
| 147 |
-
python -m sglang.launch_server --model-path Qwen/Qwen3-4B
|
| 148 |
```
|
| 149 |
- vLLM:
|
| 150 |
```shell
|
| 151 |
-
vllm serve Qwen/Qwen3-4B
|
| 152 |
```
|
| 153 |
|
| 154 |
-
**Note: If you encounter out-of-memory (OOM) issues, you may consider reducing the context length to a smaller value. However, since the model may require longer token sequences for reasoning, we strongly recommend using a context length greater than 131,072 when possible.**
|
| 155 |
-
|
| 156 |
For local use, applications such as Ollama, LMStudio, MLX-LM, llama.cpp, and KTransformers have also supported Qwen3.
|
| 157 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 158 |
## Agentic Use
|
| 159 |
|
| 160 |
Qwen3 excels in tool calling capabilities. We recommend using [Qwen-Agent](https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen-Agent) to make the best use of agentic ability of Qwen3. Qwen-Agent encapsulates tool-calling templates and tool-calling parsers internally, greatly reducing coding complexity.
|
|
@@ -164,18 +222,23 @@ To define the available tools, you can use the MCP configuration file, use the i
|
|
| 164 |
from qwen_agent.agents import Assistant
|
| 165 |
|
| 166 |
# Define LLM
|
| 167 |
-
# Using OpenAI-compatible API endpoint. It is recommended to disable the reasoning and the tool call parsing
|
| 168 |
-
# functionality of the deployment frameworks and let Qwen-Agent automate the related operations. For example,
|
| 169 |
-
# `VLLM_USE_MODELSCOPE=true vllm serve Qwen/Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507 --served-model-name Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507 --max-model-len 262144`.
|
| 170 |
llm_cfg = {
|
| 171 |
-
'model': 'Qwen3-4B
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 172 |
|
| 173 |
# Use a custom endpoint compatible with OpenAI API:
|
| 174 |
-
'model_server': 'http://localhost:8000/v1', # api_base
|
| 175 |
'api_key': 'EMPTY',
|
| 176 |
-
|
| 177 |
-
|
| 178 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 179 |
}
|
| 180 |
|
| 181 |
# Define Tools
|
|
@@ -204,15 +267,71 @@ for responses in bot.run(messages=messages):
|
|
| 204 |
print(responses)
|
| 205 |
```
|
| 206 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 207 |
## Best Practices
|
| 208 |
|
| 209 |
To achieve optimal performance, we recommend the following settings:
|
| 210 |
|
| 211 |
1. **Sampling Parameters**:
|
| 212 |
-
-
|
|
|
|
| 213 |
- For supported frameworks, you can adjust the `presence_penalty` parameter between 0 and 2 to reduce endless repetitions. However, using a higher value may occasionally result in language mixing and a slight decrease in model performance.
|
| 214 |
|
| 215 |
-
2. **Adequate Output Length**: We recommend using an output length of 32,768 tokens for most queries. For benchmarking on highly complex problems, such as those found in math and programming competitions, we suggest setting the max output length to
|
| 216 |
|
| 217 |
3. **Standardize Output Format**: We recommend using prompts to standardize model outputs when benchmarking.
|
| 218 |
- **Math Problems**: Include "Please reason step by step, and put your final answer within \boxed{}." in the prompt.
|
|
@@ -220,7 +339,6 @@ To achieve optimal performance, we recommend the following settings:
|
|
| 220 |
|
| 221 |
4. **No Thinking Content in History**: In multi-turn conversations, the historical model output should only include the final output part and does not need to include the thinking content. It is implemented in the provided chat template in Jinja2. However, for frameworks that do not directly use the Jinja2 chat template, it is up to the developers to ensure that the best practice is followed.
|
| 222 |
|
| 223 |
-
|
| 224 |
### Citation
|
| 225 |
|
| 226 |
If you find our work helpful, feel free to give us a cite.
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
---
|
| 2 |
+
library_name: transformers
|
| 3 |
license: apache-2.0
|
| 4 |
+
license_link: https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen3-4B/blob/main/LICENSE
|
| 5 |
+
pipeline_tag: text-generation
|
| 6 |
base_model:
|
| 7 |
+
- Qwen/Qwen3-4B-Base
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 8 |
---
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
+
# Qwen3-4B
|
| 11 |
<a href="https://chat.qwen.ai/" target="_blank" style="margin: 2px;">
|
| 12 |
<img alt="Chat" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%92%9C%EF%B8%8F%20Qwen%20Chat%20-536af5" style="display: inline-block; vertical-align: middle;"/>
|
| 13 |
</a>
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
+
## Qwen3 Highlights
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
+
Qwen3 is the latest generation of large language models in Qwen series, offering a comprehensive suite of dense and mixture-of-experts (MoE) models. Built upon extensive training, Qwen3 delivers groundbreaking advancements in reasoning, instruction-following, agent capabilities, and multilingual support, with the following key features:
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
+
- **Uniquely support of seamless switching between thinking mode** (for complex logical reasoning, math, and coding) and **non-thinking mode** (for efficient, general-purpose dialogue) **within single model**, ensuring optimal performance across various scenarios.
|
| 20 |
+
- **Significantly enhancement in its reasoning capabilities**, surpassing previous QwQ (in thinking mode) and Qwen2.5 instruct models (in non-thinking mode) on mathematics, code generation, and commonsense logical reasoning.
|
| 21 |
+
- **Superior human preference alignment**, excelling in creative writing, role-playing, multi-turn dialogues, and instruction following, to deliver a more natural, engaging, and immersive conversational experience.
|
| 22 |
+
- **Expertise in agent capabilities**, enabling precise integration with external tools in both thinking and unthinking modes and achieving leading performance among open-source models in complex agent-based tasks.
|
| 23 |
+
- **Support of 100+ languages and dialects** with strong capabilities for **multilingual instruction following** and **translation**.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
## Model Overview
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
+
**Qwen3-4B** has the following features:
|
| 28 |
- Type: Causal Language Models
|
| 29 |
- Training Stage: Pretraining & Post-training
|
| 30 |
- Number of Parameters: 4.0B
|
| 31 |
- Number of Paramaters (Non-Embedding): 3.6B
|
| 32 |
- Number of Layers: 36
|
| 33 |
- Number of Attention Heads (GQA): 32 for Q and 8 for KV
|
| 34 |
+
- Context Length: 32,768 natively and [131,072 tokens with YaRN](#processing-long-texts).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
For more details, including benchmark evaluation, hardware requirements, and inference performance, please refer to our [blog](https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/qwen3/), [GitHub](https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3), and [Documentation](https://qwen.readthedocs.io/en/latest/).
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 39 |
+
> If you encounter significant endless repetitions, please refer to the [Best Practices](#best-practices) section for optimal sampling parameters, and set the ``presence_penalty`` to 1.5.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 40 |
|
| 41 |
## Quickstart
|
| 42 |
|
|
|
|
| 51 |
```python
|
| 52 |
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
| 53 |
|
| 54 |
+
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen3-4B"
|
| 55 |
|
| 56 |
# load the tokenizer and the model
|
| 57 |
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
|
|
|
| 70 |
messages,
|
| 71 |
tokenize=False,
|
| 72 |
add_generation_prompt=True,
|
| 73 |
+
enable_thinking=True # Switches between thinking and non-thinking modes. Default is True.
|
| 74 |
)
|
| 75 |
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
|
| 76 |
|
|
|
|
| 91 |
thinking_content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[:index], skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
|
| 92 |
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[index:], skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
|
| 93 |
|
| 94 |
+
print("thinking content:", thinking_content)
|
| 95 |
print("content:", content)
|
|
|
|
| 96 |
```
|
| 97 |
|
| 98 |
For deployment, you can use `sglang>=0.4.6.post1` or `vllm>=0.8.5` or to create an OpenAI-compatible API endpoint:
|
| 99 |
- SGLang:
|
| 100 |
```shell
|
| 101 |
+
python -m sglang.launch_server --model-path Qwen/Qwen3-4B --reasoning-parser qwen3
|
| 102 |
```
|
| 103 |
- vLLM:
|
| 104 |
```shell
|
| 105 |
+
vllm serve Qwen/Qwen3-4B --enable-reasoning --reasoning-parser deepseek_r1
|
| 106 |
```
|
| 107 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 108 |
For local use, applications such as Ollama, LMStudio, MLX-LM, llama.cpp, and KTransformers have also supported Qwen3.
|
| 109 |
|
| 110 |
+
## Switching Between Thinking and Non-Thinking Mode
|
| 111 |
+
|
| 112 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 113 |
+
> The `enable_thinking` switch is also available in APIs created by SGLang and vLLM.
|
| 114 |
+
> Please refer to our documentation for [SGLang](https://qwen.readthedocs.io/en/latest/deployment/sglang.html#thinking-non-thinking-modes) and [vLLM](https://qwen.readthedocs.io/en/latest/deployment/vllm.html#thinking-non-thinking-modes) users.
|
| 115 |
+
|
| 116 |
+
### `enable_thinking=True`
|
| 117 |
+
|
| 118 |
+
By default, Qwen3 has thinking capabilities enabled, similar to QwQ-32B. This means the model will use its reasoning abilities to enhance the quality of generated responses. For example, when explicitly setting `enable_thinking=True` or leaving it as the default value in `tokenizer.apply_chat_template`, the model will engage its thinking mode.
|
| 119 |
+
|
| 120 |
+
```python
|
| 121 |
+
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
|
| 122 |
+
messages,
|
| 123 |
+
tokenize=False,
|
| 124 |
+
add_generation_prompt=True,
|
| 125 |
+
enable_thinking=True # True is the default value for enable_thinking
|
| 126 |
+
)
|
| 127 |
+
```
|
| 128 |
+
|
| 129 |
+
In this mode, the model will generate think content wrapped in a `<think>...</think>` block, followed by the final response.
|
| 130 |
+
|
| 131 |
+
> [!NOTE]
|
| 132 |
+
> For thinking mode, use `Temperature=0.6`, `TopP=0.95`, `TopK=20`, and `MinP=0` (the default setting in `generation_config.json`). **DO NOT use greedy decoding**, as it can lead to performance degradation and endless repetitions. For more detailed guidance, please refer to the [Best Practices](#best-practices) section.
|
| 133 |
+
|
| 134 |
+
|
| 135 |
+
### `enable_thinking=False`
|
| 136 |
+
|
| 137 |
+
We provide a hard switch to strictly disable the model's thinking behavior, aligning its functionality with the previous Qwen2.5-Instruct models. This mode is particularly useful in scenarios where disabling thinking is essential for enhancing efficiency.
|
| 138 |
+
|
| 139 |
+
```python
|
| 140 |
+
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
|
| 141 |
+
messages,
|
| 142 |
+
tokenize=False,
|
| 143 |
+
add_generation_prompt=True,
|
| 144 |
+
enable_thinking=False # Setting enable_thinking=False disables thinking mode
|
| 145 |
+
)
|
| 146 |
+
```
|
| 147 |
+
|
| 148 |
+
In this mode, the model will not generate any think content and will not include a `<think>...</think>` block.
|
| 149 |
+
|
| 150 |
+
> [!NOTE]
|
| 151 |
+
> For non-thinking mode, we suggest using `Temperature=0.7`, `TopP=0.8`, `TopK=20`, and `MinP=0`. For more detailed guidance, please refer to the [Best Practices](#best-practices) section.
|
| 152 |
+
|
| 153 |
+
### Advanced Usage: Switching Between Thinking and Non-Thinking Modes via User Input
|
| 154 |
+
|
| 155 |
+
We provide a soft switch mechanism that allows users to dynamically control the model's behavior when `enable_thinking=True`. Specifically, you can add `/think` and `/no_think` to user prompts or system messages to switch the model's thinking mode from turn to turn. The model will follow the most recent instruction in multi-turn conversations.
|
| 156 |
+
|
| 157 |
+
Here is an example of a multi-turn conversation:
|
| 158 |
+
|
| 159 |
+
```python
|
| 160 |
+
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
| 161 |
+
|
| 162 |
+
class QwenChatbot:
|
| 163 |
+
def __init__(self, model_name="Qwen/Qwen3-4B"):
|
| 164 |
+
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
| 165 |
+
self.model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
| 166 |
+
self.history = []
|
| 167 |
+
|
| 168 |
+
def generate_response(self, user_input):
|
| 169 |
+
messages = self.history + [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]
|
| 170 |
+
|
| 171 |
+
text = self.tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
|
| 172 |
+
messages,
|
| 173 |
+
tokenize=False,
|
| 174 |
+
add_generation_prompt=True
|
| 175 |
+
)
|
| 176 |
+
|
| 177 |
+
inputs = self.tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt")
|
| 178 |
+
response_ids = self.model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=32768)[0][len(inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
|
| 179 |
+
response = self.tokenizer.decode(response_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
| 180 |
+
|
| 181 |
+
# Update history
|
| 182 |
+
self.history.append({"role": "user", "content": user_input})
|
| 183 |
+
self.history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": response})
|
| 184 |
+
|
| 185 |
+
return response
|
| 186 |
+
|
| 187 |
+
# Example Usage
|
| 188 |
+
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
| 189 |
+
chatbot = QwenChatbot()
|
| 190 |
+
|
| 191 |
+
# First input (without /think or /no_think tags, thinking mode is enabled by default)
|
| 192 |
+
user_input_1 = "How many r's in strawberries?"
|
| 193 |
+
print(f"User: {user_input_1}")
|
| 194 |
+
response_1 = chatbot.generate_response(user_input_1)
|
| 195 |
+
print(f"Bot: {response_1}")
|
| 196 |
+
print("----------------------")
|
| 197 |
+
|
| 198 |
+
# Second input with /no_think
|
| 199 |
+
user_input_2 = "Then, how many r's in blueberries? /no_think"
|
| 200 |
+
print(f"User: {user_input_2}")
|
| 201 |
+
response_2 = chatbot.generate_response(user_input_2)
|
| 202 |
+
print(f"Bot: {response_2}")
|
| 203 |
+
print("----------------------")
|
| 204 |
+
|
| 205 |
+
# Third input with /think
|
| 206 |
+
user_input_3 = "Really? /think"
|
| 207 |
+
print(f"User: {user_input_3}")
|
| 208 |
+
response_3 = chatbot.generate_response(user_input_3)
|
| 209 |
+
print(f"Bot: {response_3}")
|
| 210 |
+
```
|
| 211 |
+
|
| 212 |
+
> [!NOTE]
|
| 213 |
+
> For API compatibility, when `enable_thinking=True`, regardless of whether the user uses `/think` or `/no_think`, the model will always output a block wrapped in `<think>...</think>`. However, the content inside this block may be empty if thinking is disabled.
|
| 214 |
+
> When `enable_thinking=False`, the soft switches are not valid. Regardless of any `/think` or `/no_think` tags input by the user, the model will not generate think content and will not include a `<think>...</think>` block.
|
| 215 |
+
|
| 216 |
## Agentic Use
|
| 217 |
|
| 218 |
Qwen3 excels in tool calling capabilities. We recommend using [Qwen-Agent](https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen-Agent) to make the best use of agentic ability of Qwen3. Qwen-Agent encapsulates tool-calling templates and tool-calling parsers internally, greatly reducing coding complexity.
|
|
|
|
| 222 |
from qwen_agent.agents import Assistant
|
| 223 |
|
| 224 |
# Define LLM
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 225 |
llm_cfg = {
|
| 226 |
+
'model': 'Qwen3-4B',
|
| 227 |
+
|
| 228 |
+
# Use the endpoint provided by Alibaba Model Studio:
|
| 229 |
+
# 'model_type': 'qwen_dashscope',
|
| 230 |
+
# 'api_key': os.getenv('DASHSCOPE_API_KEY'),
|
| 231 |
|
| 232 |
# Use a custom endpoint compatible with OpenAI API:
|
| 233 |
+
'model_server': 'http://localhost:8000/v1', # api_base
|
| 234 |
'api_key': 'EMPTY',
|
| 235 |
+
|
| 236 |
+
# Other parameters:
|
| 237 |
+
# 'generate_cfg': {
|
| 238 |
+
# # Add: When the response content is `<think>this is the thought</think>this is the answer;
|
| 239 |
+
# # Do not add: When the response has been separated by reasoning_content and content.
|
| 240 |
+
# 'thought_in_content': True,
|
| 241 |
+
# },
|
| 242 |
}
|
| 243 |
|
| 244 |
# Define Tools
|
|
|
|
| 267 |
print(responses)
|
| 268 |
```
|
| 269 |
|
| 270 |
+
## Processing Long Texts
|
| 271 |
+
|
| 272 |
+
Qwen3 natively supports context lengths of up to 32,768 tokens. For conversations where the total length (including both input and output) significantly exceeds this limit, we recommend using RoPE scaling techniques to handle long texts effectively. We have validated the model's performance on context lengths of up to 131,072 tokens using the [YaRN](https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.00071) method.
|
| 273 |
+
|
| 274 |
+
YaRN is currently supported by several inference frameworks, e.g., `transformers` and `llama.cpp` for local use, `vllm` and `sglang` for deployment. In general, there are two approaches to enabling YaRN for supported frameworks:
|
| 275 |
+
|
| 276 |
+
- Modifying the model files:
|
| 277 |
+
In the `config.json` file, add the `rope_scaling` fields:
|
| 278 |
+
```json
|
| 279 |
+
{
|
| 280 |
+
...,
|
| 281 |
+
"rope_scaling": {
|
| 282 |
+
"rope_type": "yarn",
|
| 283 |
+
"factor": 4.0,
|
| 284 |
+
"original_max_position_embeddings": 32768
|
| 285 |
+
}
|
| 286 |
+
}
|
| 287 |
+
```
|
| 288 |
+
For `llama.cpp`, you need to regenerate the GGUF file after the modification.
|
| 289 |
+
|
| 290 |
+
- Passing command line arguments:
|
| 291 |
+
|
| 292 |
+
For `vllm`, you can use
|
| 293 |
+
```shell
|
| 294 |
+
vllm serve ... --rope-scaling '{"rope_type":"yarn","factor":4.0,"original_max_position_embeddings":32768}' --max-model-len 131072
|
| 295 |
+
```
|
| 296 |
+
|
| 297 |
+
For `sglang`, you can use
|
| 298 |
+
```shell
|
| 299 |
+
python -m sglang.launch_server ... --json-model-override-args '{"rope_scaling":{"rope_type":"yarn","factor":4.0,"original_max_position_embeddings":32768}}'
|
| 300 |
+
```
|
| 301 |
+
|
| 302 |
+
For `llama-server` from `llama.cpp`, you can use
|
| 303 |
+
```shell
|
| 304 |
+
llama-server ... --rope-scaling yarn --rope-scale 4 --yarn-orig-ctx 32768
|
| 305 |
+
```
|
| 306 |
+
|
| 307 |
+
> [!IMPORTANT]
|
| 308 |
+
> If you encounter the following warning
|
| 309 |
+
> ```
|
| 310 |
+
> Unrecognized keys in `rope_scaling` for 'rope_type'='yarn': {'original_max_position_embeddings'}
|
| 311 |
+
> ```
|
| 312 |
+
> please upgrade `transformers>=4.51.0`.
|
| 313 |
+
|
| 314 |
+
> [!NOTE]
|
| 315 |
+
> All the notable open-source frameworks implement static YaRN, which means the scaling factor remains constant regardless of input length, **potentially impacting performance on shorter texts.**
|
| 316 |
+
> We advise adding the `rope_scaling` configuration only when processing long contexts is required.
|
| 317 |
+
> It is also recommended to modify the `factor` as needed. For example, if the typical context length for your application is 65,536 tokens, it would be better to set `factor` as 2.0.
|
| 318 |
+
|
| 319 |
+
> [!NOTE]
|
| 320 |
+
> The default `max_position_embeddings` in `config.json` is set to 40,960. This allocation includes reserving 32,768 tokens for outputs and 8,192 tokens for typical prompts, which is sufficient for most scenarios involving short text processing. If the average context length does not exceed 32,768 tokens, we do not recommend enabling YaRN in this scenario, as it may potentially degrade model performance.
|
| 321 |
+
|
| 322 |
+
> [!TIP]
|
| 323 |
+
> The endpoint provided by Alibaba Model Studio supports dynamic YaRN by default and no extra configuration is needed.
|
| 324 |
+
|
| 325 |
## Best Practices
|
| 326 |
|
| 327 |
To achieve optimal performance, we recommend the following settings:
|
| 328 |
|
| 329 |
1. **Sampling Parameters**:
|
| 330 |
+
- For thinking mode (`enable_thinking=True`), use `Temperature=0.6`, `TopP=0.95`, `TopK=20`, and `MinP=0`. **DO NOT use greedy decoding**, as it can lead to performance degradation and endless repetitions.
|
| 331 |
+
- For non-thinking mode (`enable_thinking=False`), we suggest using `Temperature=0.7`, `TopP=0.8`, `TopK=20`, and `MinP=0`.
|
| 332 |
- For supported frameworks, you can adjust the `presence_penalty` parameter between 0 and 2 to reduce endless repetitions. However, using a higher value may occasionally result in language mixing and a slight decrease in model performance.
|
| 333 |
|
| 334 |
+
2. **Adequate Output Length**: We recommend using an output length of 32,768 tokens for most queries. For benchmarking on highly complex problems, such as those found in math and programming competitions, we suggest setting the max output length to 38,912 tokens. This provides the model with sufficient space to generate detailed and comprehensive responses, thereby enhancing its overall performance.
|
| 335 |
|
| 336 |
3. **Standardize Output Format**: We recommend using prompts to standardize model outputs when benchmarking.
|
| 337 |
- **Math Problems**: Include "Please reason step by step, and put your final answer within \boxed{}." in the prompt.
|
|
|
|
| 339 |
|
| 340 |
4. **No Thinking Content in History**: In multi-turn conversations, the historical model output should only include the final output part and does not need to include the thinking content. It is implemented in the provided chat template in Jinja2. However, for frameworks that do not directly use the Jinja2 chat template, it is up to the developers to ensure that the best practice is followed.
|
| 341 |
|
|
|
|
| 342 |
### Citation
|
| 343 |
|
| 344 |
If you find our work helpful, feel free to give us a cite.
|