Update README.md
Browse files
README.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -29,3 +29,44 @@ configs:
|
|
| 29 |
- split: train
|
| 30 |
path: data/train-*
|
| 31 |
---
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 29 |
- split: train
|
| 30 |
path: data/train-*
|
| 31 |
---
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
---
|
| 34 |
+
* **`2024.11.14`** 🌟 MME-RealWorld now has a [lite version](https://huggingface.co/datasets/yifanzhang114/MME-RealWorld-Lite) (50 samples per task) for inference acceleration, which is also supported by VLMEvalKit and Lmms-eval.
|
| 35 |
+
* **`2024.10.27`** 🌟 LLaVA-OV currently ranks first on our leaderboard, but its overall accuracy remains below 55%, see our [leaderboard](https://mme-realworld.github.io/home_page.html#leaderboard) for the detail.
|
| 36 |
+
* **`2024.09.03`** 🌟 MME-RealWorld is now supported in the [VLMEvalKit](https://github.com/open-compass/VLMEvalKit) and [Lmms-eval](https://github.com/EvolvingLMMs-Lab/lmms-eval) repository, enabling one-click evaluation—give it a try!"
|
| 37 |
+
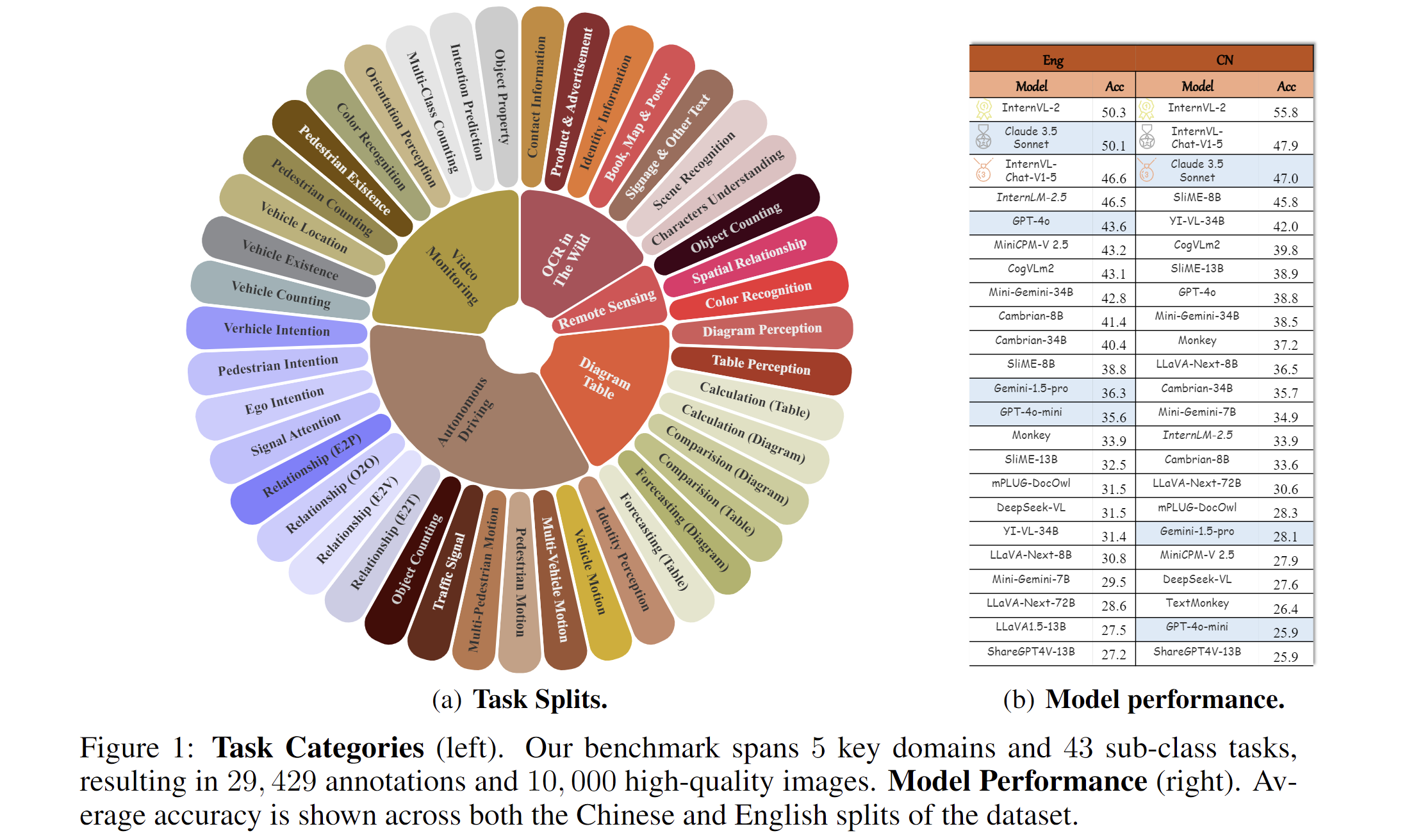
* **`2024.08.20`** 🌟 We are very proud to launch MME-RealWorld, which contains 13K high-quality images, annotated by 32 volunteers, resulting in 29K question-answer pairs that cover 43 subtasks across 5 real-world scenarios. As far as we know, **MME-RealWorld is the largest manually annotated benchmark to date, featuring the highest resolution and a targeted focus on real-world applications**.
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2408.13257
|
| 41 |
+
|
| 42 |
+
Code: https://github.com/yfzhang114/MME-RealWorld
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
Project page: https://mme-realworld.github.io/
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+

|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
# MME-RealWorld Data Card
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
## Dataset details
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
|
| 55 |
+
Existing Multimodal Large Language Model benchmarks present several common barriers that make it difficult to measure the significant challenges that models face in the real world, including:
|
| 56 |
+
1) small data scale leads to a large performance variance;
|
| 57 |
+
2) reliance on model-based annotations results in restricted data quality;
|
| 58 |
+
3) insufficient task difficulty, especially caused by the limited image resolution.
|
| 59 |
+
|
| 60 |
+
We present MME-RealWord, a benchmark meticulously designed to address real-world applications with practical relevance. Featuring 13,366 high-resolution images averaging 2,000 × 1,500 pixels, MME-RealWord poses substantial recognition challenges. Our dataset encompasses 29,429 annotations across 43 tasks, all expertly curated by a team of 25 crowdsource workers and 7 MLLM experts. The main advantages of MME-RealWorld compared to existing MLLM benchmarks as follows:
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
1. **Data Scale**: with the efforts of a total of 32 volunteers, we have manually annotated 29,429 QA pairs focused on real-world scenarios, making this the largest fully human-annotated benchmark known to date.
|
| 63 |
+
|
| 64 |
+
2. **Data Quality**: 1) Resolution: Many image details, such as a scoreboard in a sports event, carry critical information. These details can only be properly interpreted with high- resolution images, which are essential for providing meaningful assistance to humans. To the best of our knowledge, MME-RealWorld features the highest average image resolution among existing competitors. 2) Annotation: All annotations are manually completed, with a professional team cross-checking the results to ensure data quality.
|
| 65 |
+
|
| 66 |
+
3. **Task Difficulty and Real-World Utility.**: We can see that even the most advanced models have not surpassed 60% accuracy. Additionally, many real-world tasks are significantly more difficult than those in traditional benchmarks. For example, in video monitoring, a model needs to count the presence of 133 vehicles, or in remote sensing, it must identify and count small objects on a map with an average resolution exceeding 5000×5000.
|
| 67 |
+
|
| 68 |
+
4. **MME-RealWord-CN.**: Existing Chinese benchmark is usually translated from its English version. This has two limitations: 1) Question-image mismatch. The image may relate to an English scenario, which is not intuitively connected to a Chinese question. 2) Translation mismatch [58]. The machine translation is not always precise and perfect enough. We collect additional images that focus on Chinese scenarios, asking Chinese volunteers for annotation. This results in 5,917 QA pairs.
|
| 69 |
+
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
|
| 72 |
+
|