Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct-FP8

Highlights
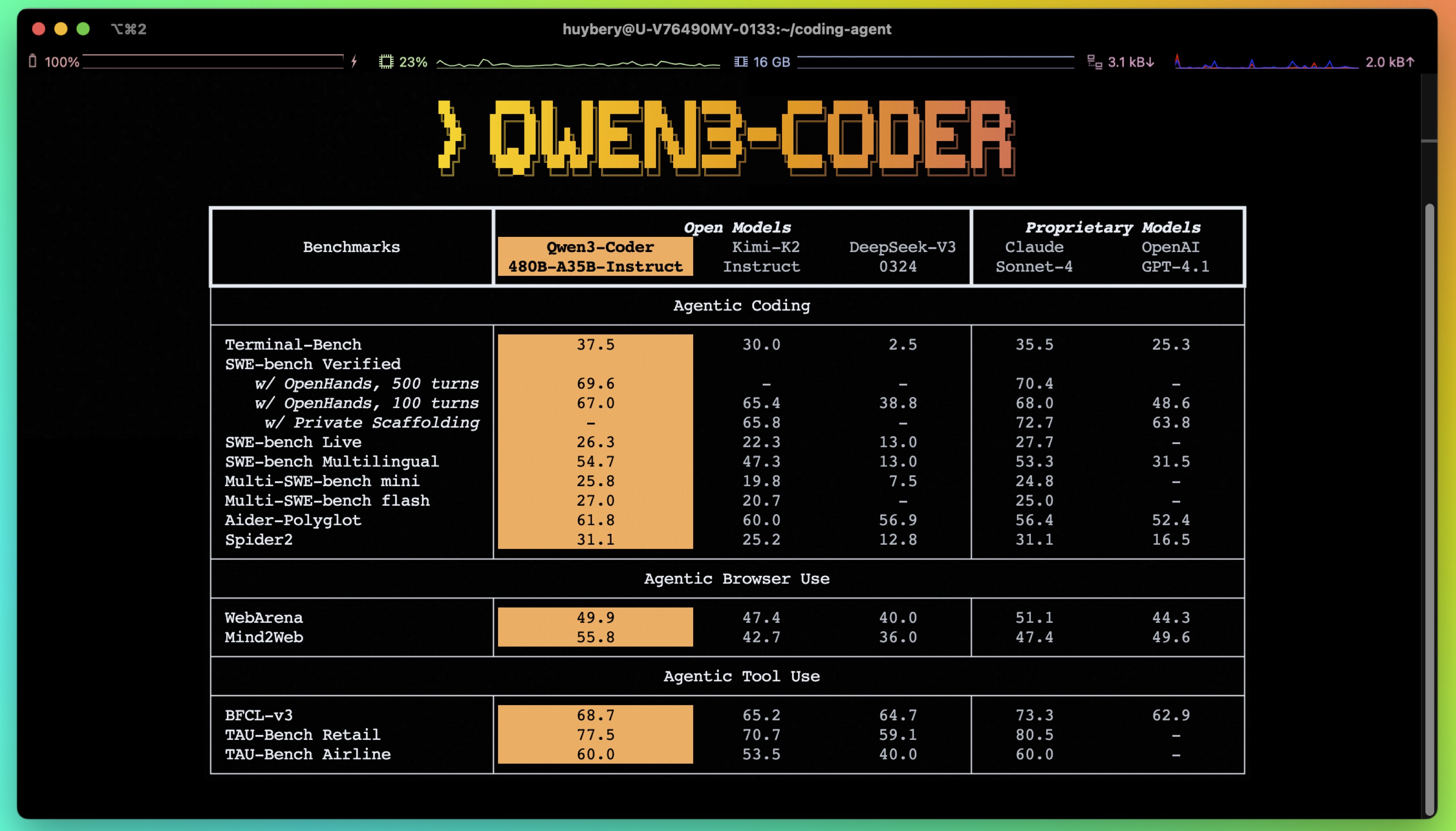
Today, we're announcing Qwen3-Coder, our most agentic code model to date. Qwen3-Coder is available in multiple sizes, but we're excited to introduce its most powerful variant first: Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct. featuring the following key enhancements:
- Significant Performance among open models on Agentic Coding, Agentic Browser-Use, and other foundational coding tasks, achieving results comparable to Claude Sonnet.
- Long-context Capabilities with native support for 256K tokens, extendable up to 1M tokens using Yarn, optimized for repository-scale understanding.
- Agentic Coding supporting for most platform such as Qwen Code, CLINE, featuring a specially designed function call format.
Model Overview
Qwen3-480B-A35B-Instruct has the following features:
- Type: Causal Language Models
- Training Stage: Pretraining & Post-training
- Number of Parameters: 480B in total and 35B activated
- Number of Layers: 62
- Number of Attention Heads (GQA): 96 for Q and 8 for KV
- Number of Experts: 160
- Number of Activated Experts: 8
- Context Length: 262,144 natively.
NOTE: This model supports only non-thinking mode and does not generate <think></think> blocks in its output. Meanwhile, specifying enable_thinking=False is no longer required.
For more details, including benchmark evaluation, hardware requirements, and inference performance, please refer to our blog, GitHub, and Documentation.
Quickstart
We advise you to use the latest version of transformers.
With transformers<4.51.0, you will encounter the following error:
KeyError: 'qwen3_moe'
The following contains a code snippet illustrating how to use the model generate content based on given inputs.
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen3-480B-A35B-Instruct"
# load the tokenizer and the model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
# prepare the model input
prompt = "Write a quick sort algorithm."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# conduct text completion
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=65536
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
print("content:", content)
Note: If you encounter out-of-memory (OOM) issues, consider reducing the context length to a shorter value, such as 32,768.
Deployment
This model can be deployed efficiently using the vLLM backend, as shown in the example below.
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
model_id = "RedHatAI/Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct-FP8"
number_gpus = 8
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.6, top_p=0.95, max_tokens=1024)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language model."
llm = LLM(model=model_id, tensor_parallel_size=number_gpus)
outputs = llm.generate(prompt, sampling_params)
generated_text = outputs[0].outputs[0].text
print(generated_text)
vLLM also supports OpenAI-compatible serving. See the documentation for more details.
Deploy on Red Hat AI Inference Server
podman run --rm -it --device nvidia.com/gpu=all -p 8000:8000 \
--ipc=host \
--env "HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN=$HF_TOKEN" \
--env "HF_HUB_OFFLINE=0" -v ~/.cache/vllm:/home/vllm/.cache \
--name=vllm \
registry.access.redhat.com/rhaiis/rh-vllm-cuda \
vllm serve \
--tensor-parallel-size 8 \
--max-model-len 32768 \
--enforce-eager --model RedHatAI/Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct-FP8
Deploy on Red Hat Openshift AI
# Setting up vllm server with ServingRuntime
# Save as: vllm-servingruntime.yaml
apiVersion: serving.kserve.io/v1alpha1
kind: ServingRuntime
metadata:
name: vllm-cuda-runtime # OPTIONAL CHANGE: set a unique name
annotations:
openshift.io/display-name: vLLM NVIDIA GPU ServingRuntime for KServe
opendatahub.io/recommended-accelerators: '["nvidia.com/gpu"]'
labels:
opendatahub.io/dashboard: 'true'
spec:
annotations:
prometheus.io/port: '8080'
prometheus.io/path: '/metrics'
multiModel: false
supportedModelFormats:
- autoSelect: true
name: vLLM
containers:
- name: kserve-container
image: quay.io/modh/vllm:rhoai-2.25-cuda # CHANGE if needed. If AMD: quay.io/modh/vllm:rhoai-2.25-rocm
command:
- python
- -m
- vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server
args:
- "--port=8080"
- "--model=/mnt/models"
- "--served-model-name={{.Name}}"
env:
- name: HF_HOME
value: /tmp/hf_home
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
# Attach model to vllm server. This is an NVIDIA template
# Save as: inferenceservice.yaml
apiVersion: serving.kserve.io/v1beta1
kind: InferenceService
metadata:
annotations:
openshift.io/display-name: Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct-FP8 # OPTIONAL CHANGE
serving.kserve.io/deploymentMode: RawDeployment
name: Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct-FP8 # specify model name. This value will be used to invoke the model in the payload
labels:
opendatahub.io/dashboard: 'true'
spec:
predictor:
maxReplicas: 1
minReplicas: 1
model:
modelFormat:
name: vLLM
name: ''
resources:
limits:
cpu: '2' # this is model specific
memory: 8Gi # this is model specific
nvidia.com/gpu: '1' # this is accelerator specific
requests: # same comment for this block
cpu: '1'
memory: 4Gi
nvidia.com/gpu: '1'
runtime: vllm-cuda-runtime # must match the ServingRuntime name above
storageUri: oci://registry.redhat.io/rhelai1/modelcar-qwen3-coder-480b-a35b-instruct-fp8:1.5
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: nvidia.com/gpu
operator: Exists
# make sure first to be in the project where you want to deploy the model
# oc project <project-name>
# apply both resources to run model
# Apply the ServingRuntime
oc apply -f vllm-servingruntime.yaml
# Replace <inference-service-name> and <cluster-ingress-domain> below:
# - Run `oc get inferenceservice` to find your URL if unsure.
# Call the server using curl:
curl https://<inference-service-name>-predictor-default.<domain>/v1/chat/completions
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct-FP8",
"stream": true,
"stream_options": {
"include_usage": true
},
"max_tokens": 1,
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "How can a bee fly when its wings are so small?"
}
]
}'
See Red Hat Openshift AI documentation for more details.
Note on FP8
For convenience and performance, we have provided fp8-quantized model checkpoint for Qwen3, whose name ends with -FP8. The quantization method is fine-grained fp8 quantization with block size of 128. You can find more details in the quantization_config field in config.json.
You can use the Qwen3-480B-A35B-Instruct-FP8 model with serveral inference frameworks, including transformers, sglang, and vllm, as the original bfloat16 model.
However, please pay attention to the following known issues:
transformers:- there are currently issues with the "fine-grained fp8" method in
transformersfor distributed inference. You may need to set the environment variableCUDA_LAUNCH_BLOCKING=1if multiple devices are used in inference.
- there are currently issues with the "fine-grained fp8" method in
Agentic Coding
Qwen3-Coder excels in tool calling capabilities.
You can simply define or use any tools as following example.
# Your tool implementation
def square_the_number(num: float) -> dict:
return num ** 2
# Define Tools
tools=[
{
"type":"function",
"function":{
"name": "square_the_number",
"description": "output the square of the number.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"required": ["input_num"],
"properties": {
'input_num': {
'type': 'number',
'description': 'input_num is a number that will be squared'
}
},
}
}
}
]
import OpenAI
# Define LLM
client = OpenAI(
# Use a custom endpoint compatible with OpenAI API
base_url='http://localhost:8000/v1', # api_base
api_key="EMPTY"
)
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': 'square the number 1024'}]
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
messages=messages,
model="Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct",
max_tokens=65536,
tools=tools,
)
print(completion.choice[0])
Best Practices
To achieve optimal performance, we recommend the following settings:
Sampling Parameters:
- We suggest using
temperature=0.7,top_p=0.8,top_k=20,repetition_penalty=1.05.
- We suggest using
Adequate Output Length: We recommend using an output length of 65,536 tokens for most queries, which is adequate for instruct models.
Citation
If you find our work helpful, feel free to give us a cite.
@misc{qwen3technicalreport,
title={Qwen3 Technical Report},
author={Qwen Team},
year={2025},
eprint={2505.09388},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.09388},
}
- Downloads last month
- 78
Model tree for RedHatAI/Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct-FP8
Base model
Qwen/Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct