Datasets:
The viewer is disabled because this dataset repo requires arbitrary Python code execution. Please consider
removing the
loading script
and relying on
automated data support
(you can use
convert_to_parquet
from the datasets library). If this is not possible, please
open a discussion
for direct help.
Spatial457: A Diagnostic Benchmark for 6D Spatial Reasoning of Large Multimodal Models
Xingrui Wang1, Wufei Ma1, Tiezheng Zhang1, Celso M. de Melo2, Jieneng Chen1, Alan Yuille1
1 Johns Hopkins University 2 DEVCOM Army Research Laboratory
🌐 Project Page • 📄 Paper • 🤗 Dataset • 💻 Code
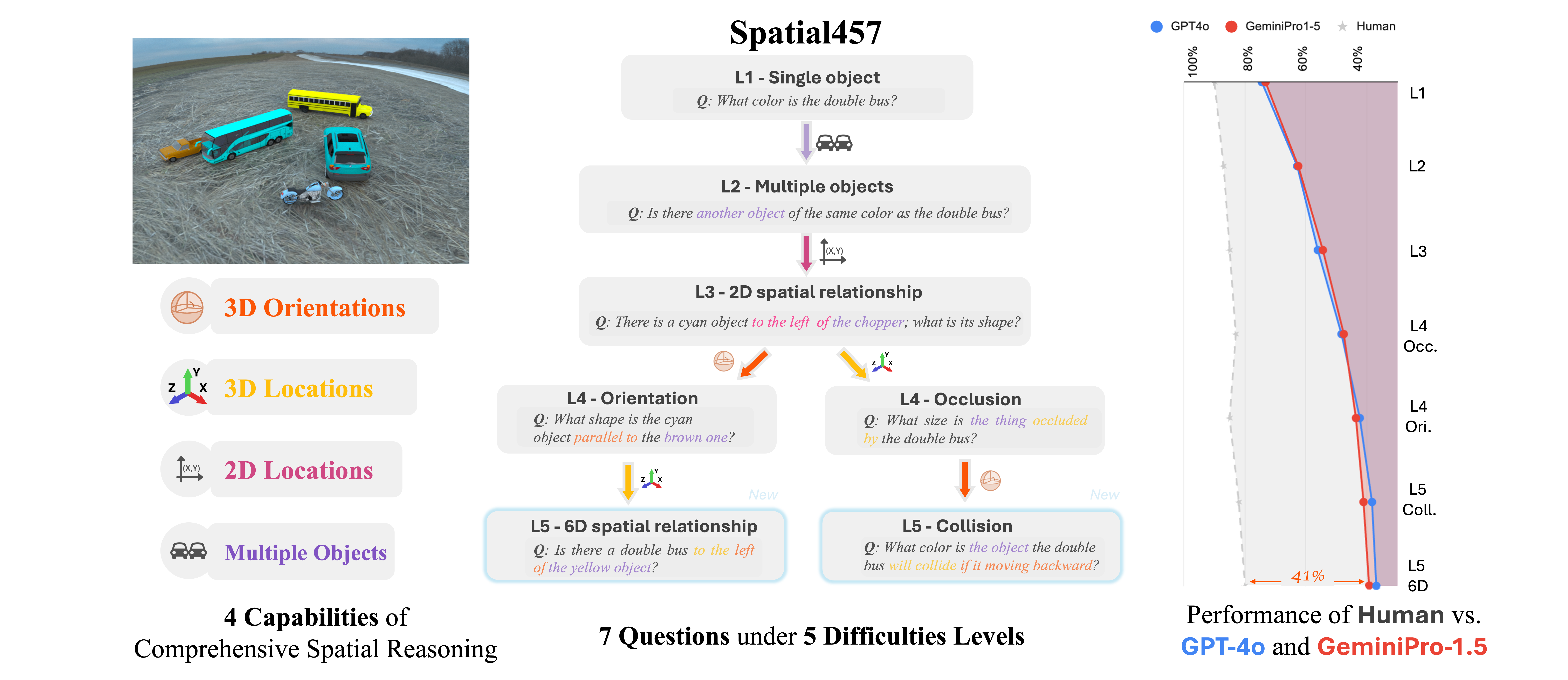
🧠 Introduction
Spatial457 is a diagnostic benchmark designed to evaluate 6D spatial reasoning in large multimodal models (LMMs). It systematically introduces four core spatial capabilities:
- 🧱 Multi-object understanding
- 🧭 2D spatial localization
- 📦 3D spatial localization
- 🔄 3D orientation estimation
These are assessed across five difficulty levels and seven diverse question types, ranging from simple object queries to complex reasoning about physical interactions.
📂 Dataset Structure
The dataset is organized as follows:
Spatial457/
├── images/ # RGB images used in VQA tasks
├── questions/ # JSONs for each subtask
│ ├── L1_single.json
│ ├── L2_objects.json
│ ├── L3_2d_spatial.json
│ ├── L4_occ.json
│ └── ...
├── Spatial457.py # Hugging Face dataset loader script
├── README.md # Documentation
Each JSON file contains a list of VQA examples, where each item includes:
- "image_filename": image file name used in the question
- "question": natural language question
- "answer": boolean, string, or number
- "program": symbolic program (optional)
- "question_index": unique identifier
This modular structure supports scalable multi-task evaluation across levels and reasoning types.
🛠️ Dataset Usage
You can load the dataset directly using the Hugging Face 🤗 datasets library:
🔹 Load a specific subtask (e.g., L5_6d_spatial)
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("RyanWW/Spatial457", name="L5_6d_spatial", split="validation", data_dir=".")
Each example is a dictionary like:
{
'image': <PIL.Image.Image>,
'image_filename': 'superCLEVR_new_000001.png',
'question': 'Is the large red object in front of the yellow car?',
'answer': 'True',
'program': [...],
'question_index': 100001
}
🔹 Other available configurations
[
"L1_single", "L2_objects", "L3_2d_spatial",
"L4_occ", "L4_pose", "L5_6d_spatial", "L5_collision"
]
You can swap name="..." in load_dataset(...) to evaluate different spatial reasoning capabilities.
📊 Benchmark
We benchmarked a wide range of state-of-the-art models—including GPT-4o, Gemini, Claude, and several open-source LMMs—across all subsets. The results below have been updated after rerunning the evaluation. While they show minor variance compared to the results in the published paper, the conclusions remain unchanged.
The inference script supports VLMEvalKit and is run by setting the dataset to Spatial457. You can find the detailed inference scripts here.
Spatial457 Evaluation Results
| Model | L1_single | L2_objects | L3_2d_spatial | L4_occ | L4_pose | L5_6d_spatial | L5_collision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4o | 72.39 | 64.54 | 58.04 | 48.87 | 43.62 | 43.06 | 44.54 |
| GeminiPro-1.5 | 69.40 | 66.73 | 55.12 | 51.41 | 44.50 | 43.11 | 44.73 |
| Claude 3.5 Sonnet | 61.04 | 59.20 | 55.20 | 40.49 | 41.38 | 38.81 | 46.27 |
| Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct | 62.84 | 58.90 | 53.73 | 26.85 | 26.83 | 36.20 | 34.84 |
📚 Citation
@inproceedings{wang2025spatial457,
title = {Spatial457: A Diagnostic Benchmark for 6D Spatial Reasoning of Large Multimodal Models},
author = {Wang, Xingrui and Ma, Wufei and Zhang, Tiezheng and de Melo, Celso M and Chen, Jieneng and Yuille, Alan},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
year = {2025},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.08636}
}
- Downloads last month
- 99