Improve language tag
#4
by
lbourdois
- opened
README.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,108 +1,122 @@
|
|
| 1 |
-
---
|
| 2 |
-
library_name: transformers
|
| 3 |
-
tags: []
|
| 4 |
-
pipeline_tag: robotics
|
| 5 |
-
license: apache-2.0
|
| 6 |
-
base_model: Qwen/Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct
|
| 7 |
-
datasets:
|
| 8 |
-
- homebrewltd/robot-hand-poses-train
|
| 9 |
-
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
-
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
|
| 15 |
-
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
|
| 18 |
-
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
|
| 21 |
-
|
| 22 |
-
|
| 23 |
-
|
| 24 |
-
|
| 25 |
-
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
|
| 30 |
-
|
| 31 |
-
|
| 32 |
-
|
| 33 |
-
|
| 34 |
-
|
| 35 |
-
|
| 36 |
-
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
|
| 39 |
-
|
| 40 |
-
|
| 41 |
-
|
| 42 |
-
|
| 43 |
-
|
| 44 |
-
|
| 45 |
-
|
| 46 |
-
|
| 47 |
-
|
| 48 |
-
|
| 49 |
-
|
| 50 |
-
|
| 51 |
-
|
| 52 |
-
|
| 53 |
-
|
| 54 |
-
|
| 55 |
-
|
| 56 |
-
|
| 57 |
-
|
| 58 |
-
|
| 59 |
-
)
|
| 60 |
-
|
| 61 |
-
|
| 62 |
-
|
| 63 |
-
|
| 64 |
-
|
| 65 |
-
|
| 66 |
-
|
| 67 |
-
|
| 68 |
-
|
| 69 |
-
|
| 70 |
-
|
| 71 |
-
|
| 72 |
-
|
| 73 |
-
|
| 74 |
-
|
| 75 |
-
|
| 76 |
-
|
| 77 |
-
|
| 78 |
-
|
| 79 |
-
|
| 80 |
-
|
| 81 |
-
|
| 82 |
-
|
| 83 |
-
|
| 84 |
-
|
| 85 |
-
|
| 86 |
-
|
| 87 |
-
|
| 88 |
-
|
| 89 |
-
|
| 90 |
-
|
| 91 |
-
|
| 92 |
-
|
| 93 |
-
|
| 94 |
-
|
| 95 |
-
|
| 96 |
-
|
| 97 |
-
|
| 98 |
-
|
| 99 |
-
|
| 100 |
-
|
| 101 |
-
|
| 102 |
-
|
| 103 |
-
|
| 104 |
-
|
| 105 |
-
|
| 106 |
-
|
| 107 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 108 |
* Contact the authors at [email protected], [email protected], [email protected], [email protected] for further details.
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
---
|
| 2 |
+
library_name: transformers
|
| 3 |
+
tags: []
|
| 4 |
+
pipeline_tag: robotics
|
| 5 |
+
license: apache-2.0
|
| 6 |
+
base_model: Qwen/Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct
|
| 7 |
+
datasets:
|
| 8 |
+
- homebrewltd/robot-hand-poses-train
|
| 9 |
+
language:
|
| 10 |
+
- zho
|
| 11 |
+
- eng
|
| 12 |
+
- fra
|
| 13 |
+
- spa
|
| 14 |
+
- por
|
| 15 |
+
- deu
|
| 16 |
+
- ita
|
| 17 |
+
- rus
|
| 18 |
+
- jpn
|
| 19 |
+
- kor
|
| 20 |
+
- vie
|
| 21 |
+
- tha
|
| 22 |
+
- ara
|
| 23 |
+
---
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
# Poseless-3B
|
| 26 |
+
|
| 27 |
+
|
| 28 |
+
|
| 29 |
+
## Introduction
|
| 30 |
+
|
| 31 |
+
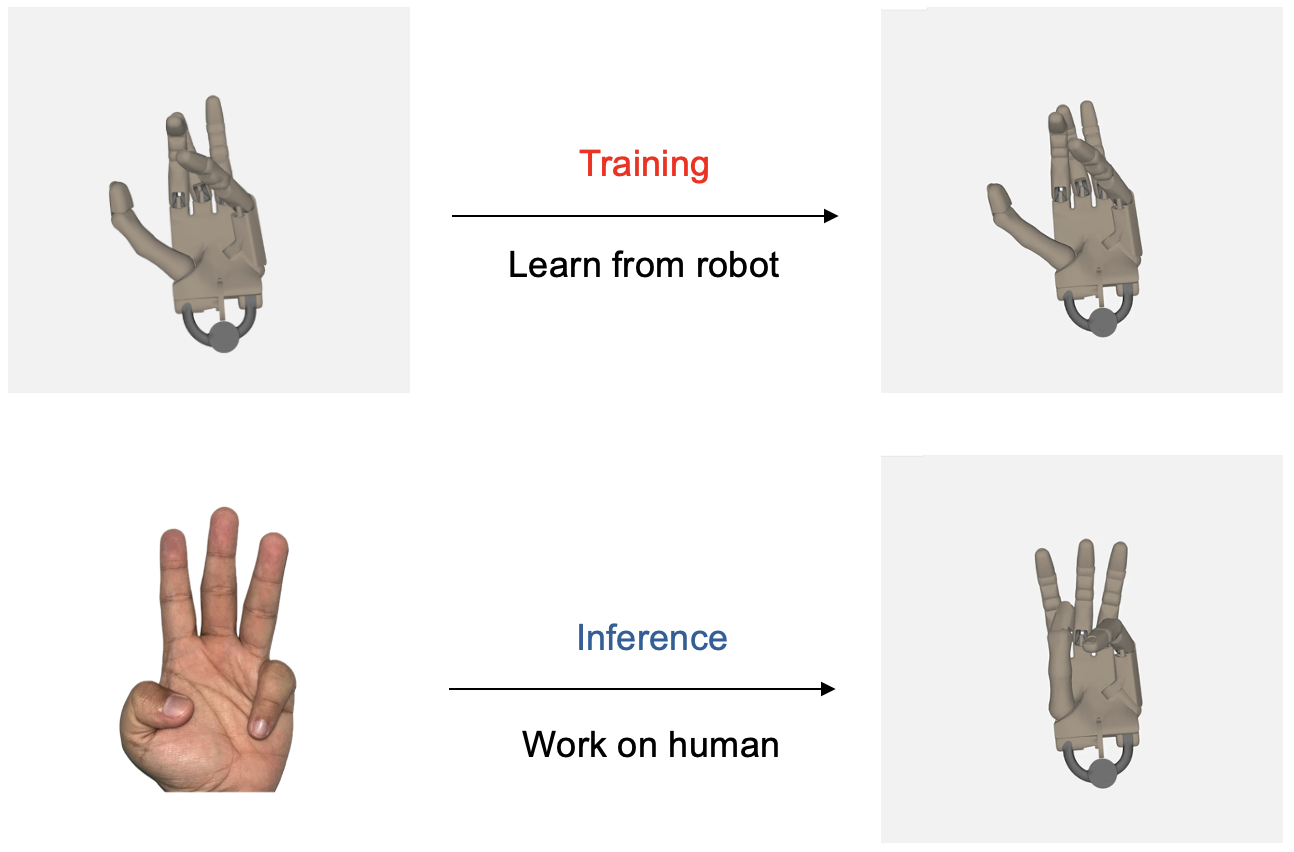
**"PoseLess: Depth-Free Vision-to-Joint Control via Direct Image Mapping with VLM"** ([Paper](https://huggingface.co/papers/2503.07111)) introduces a novel framework for robot hand control that eliminates the need for explicit pose estimation by directly mapping 2D images to joint angles using projected representations. Our approach leverages synthetic training data generated through randomized joint configurations, enabling zero-shot generalization to real-world scenarios and cross-morphology transfer from robotic to human hands. By projecting visual inputs and employing a transformer-based decoder, PoseLess achieves robust, low-latency control while addressing challenges such as depth ambiguity and data scarcity. Experimental results demonstrate competitive performance in joint angle prediction accuracy without relying on any human-labelled dataset
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
Our key contributions are as follows:
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
* We introduce a novel framework that leverages a VLM (e.g., Qwen 2.5 3B Instruct) to directly map monocular images to robot joint angles, bypassing pose estimation entirely. The VLM’s ability to "see" and project images enables robust, morphology-agnostic feature extraction, reducing error propagation inherent in two-stage pipelines.
|
| 36 |
+
* We introduce a synthetic data pipeline generates infinite training examples by randomizing joint angles and domain-randomizing visual features (e.g., lighting, textures). This eliminates reliance on costly labeled datasets while ensuring robustness to real-world variations.
|
| 37 |
+
* We provide evidence of the model’s cross-morphology generalization, demonstrating its ability to mimic human hand movements despite being trained solely on robot hand data. These findings mark a significant step toward understanding and leveraging such generalization for broader applications.
|
| 38 |
+
* We provide evidence that depth-free control is possible paving way for later adoption with camera that is not supporting depth estimation capability that is frequently used in robotics research.
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
|
| 41 |
+
## Model Details
|
| 42 |
+
* Model architecture: Qwen 2.5 3B Instruct, fine-tuned for hand pose estimation
|
| 43 |
+
* Dataset:
|
| 44 |
+
* Training: [homebrewltd/robot-hand-poses-train](https://huggingface.co/datasets/homebrewltd/robot-hand-poses-train)
|
| 45 |
+
* Eval: [homebrewltd/robotic-hand-poses-eval](https://huggingface.co/datasets/homebrewltd/robotic-hand-poses-eval)
|
| 46 |
+
* License: Apache-2.0 license
|
| 47 |
+
* Developed by: Alan Dao, Dinh Bach Vu, Tuan Le Duc Anh, Bui Quang Huy (Menlo Research)
|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
## How to Get Started
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
```python
|
| 53 |
+
import torch
|
| 54 |
+
from PIL import Image
|
| 55 |
+
from transformers import AutoProcessor, Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration
|
| 56 |
+
from qwen_vl_utils import process_vision_info
|
| 57 |
+
|
| 58 |
+
# 1. Load model and processor
|
| 59 |
+
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
|
| 60 |
+
model_path = "homebrewltd/Poseless-3B"
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
model = Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
|
| 63 |
+
model_path,
|
| 64 |
+
trust_remote_code=True,
|
| 65 |
+
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16
|
| 66 |
+
).eval().to(device)
|
| 67 |
+
|
| 68 |
+
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(
|
| 69 |
+
model_path,
|
| 70 |
+
min_pixels=256*28*28,
|
| 71 |
+
max_pixels=1280*28*28,
|
| 72 |
+
trust_remote_code=True
|
| 73 |
+
)
|
| 74 |
+
|
| 75 |
+
# 2. Prepare your image
|
| 76 |
+
image = Image.open("your_hand_image.png").convert("RGB")
|
| 77 |
+
|
| 78 |
+
# 3. Create messages
|
| 79 |
+
SYSTEM_PROMPT = """You are a specialized Vision Language Model designed to accurately estimate joint angles from hand pose images. Your task is to analyze images of a human or robotic hand and output precise angle measurements for each joint. Output joint angles in radians.
|
| 80 |
+
Output Format:
|
| 81 |
+
<lh_WRJ2>angle</lh_WRJ2><lh_WRJ1>angle</lh_WRJ1><lh_FFJ4>angle</lh_FFJ4><lh_FFJ3>angle</lh_FFJ3><lh_FFJ2>angle</lh_FFJ2><lh_FFJ1>angle</lh_FFJ1><lh_MFJ4>angle</lh_MFJ4><lh_MFJ3>angle</lh_MFJ3><lh_MFJ2>angle</lh_MFJ2><lh_MFJ1>angle</lh_MFJ1><lh_RFJ4>angle</lh_RFJ4><lh_RFJ3>angle</lh_RFJ3><lh_RFJ2>angle</lh_RFJ2><lh_RFJ1>angle</lh_RFJ1><lh_LFJ5>angle</lh_LFJ5><lh_LFJ4>angle</lh_LFJ4><lh_LFJ3>angle</lh_LFJ3><lh_LFJ2>angle</lh_LFJ2><lh_LFJ1>angle</lh_LFJ1><lh_THJ5>angle</lh_THJ5><lh_THJ4>angle</lh_THJ4><lh_THJ3>angle</lh_THJ3><lh_THJ2>angle</lh_THJ2><lh_THJ1>angle</lh_THJ1>
|
| 82 |
+
"""
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
messages = [
|
| 85 |
+
{"role": "system", "content": f"{SYSTEM_PROMPT}"},
|
| 86 |
+
{
|
| 87 |
+
"role": "user",
|
| 88 |
+
"content": [
|
| 89 |
+
{
|
| 90 |
+
"type": "image",
|
| 91 |
+
"image": image,
|
| 92 |
+
"min_pixels": 1003520,
|
| 93 |
+
"max_pixels": 1003520,
|
| 94 |
+
},
|
| 95 |
+
{"type": "text", "text": "<Pose>"},
|
| 96 |
+
],
|
| 97 |
+
},
|
| 98 |
+
]
|
| 99 |
+
|
| 100 |
+
# 4. Process and get predictions
|
| 101 |
+
text = processor.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
|
| 102 |
+
image_inputs, video_inputs = process_vision_info(messages)
|
| 103 |
+
inputs = processor(text=[text], images=image_inputs, videos=video_inputs, padding=True, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
|
| 104 |
+
|
| 105 |
+
# 5. Generate output
|
| 106 |
+
generated_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=1024)
|
| 107 |
+
generated_ids_trimmed = [out_ids[len(in_ids):] for in_ids, out_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)]
|
| 108 |
+
output_text = processor.batch_decode(generated_ids_trimmed, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)[0]
|
| 109 |
+
|
| 110 |
+
print(output_text) # This will show the joint angles in XML format
|
| 111 |
+
```
|
| 112 |
+
|
| 113 |
+
The output will be joint angles in radians in XML format:
|
| 114 |
+
```xml
|
| 115 |
+
<lh_WRJ2>angle</lh_WRJ2><lh_WRJ1>angle</lh_WRJ1><lh_FFJ4>angle</lh_FFJ4>...
|
| 116 |
+
```
|
| 117 |
+
|
| 118 |
+
## Citation
|
| 119 |
+
- arxiv.org/abs/2503.07111
|
| 120 |
+
|
| 121 |
+
## More Information
|
| 122 |
* Contact the authors at [email protected], [email protected], [email protected], [email protected] for further details.
|