title
stringlengths 17
178
| detail_url
stringlengths 27
46
| author_list
sequencelengths 0
558
| abstract
stringlengths 0
403
|
|---|---|---|---|
ICRA 2024 Cover Page | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | |
ICRA 2024 Welcome | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610403/ | [] | |
ICRA 2024 Organizing Committee | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610680/ | [] | |
ICRA 2024 Contributor Page | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | ICRA 2024 Contributor Page |
ICRA 2024 Program | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | |
ICRA 2024 Author Index | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | ICRA 2024 Author Index |
TinyMPC: Model-Predictive Control on Resource-Constrained Microcontrollers | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610987/ | [
"Khai Nguyen",
"Sam Schoedel",
"Anoushka Alavilli",
"Brian Plancher",
"Zachary Manchester",
"Khai Nguyen",
"Sam Schoedel",
"Anoushka Alavilli",
"Brian Plancher",
"Zachary Manchester"
] | Model-predictive control (MPC) is a powerful tool for controlling highly dynamic robotic systems subject to complex constraints. However, MPC is computationally demanding, and is often impractical to implement on small, resource-constrained robotic platforms. We present TinyMPC, a high-speed MPC solver with a low memory footprint targeting the microcontrollers common on small robots. Our approach ... |
A Movable Microfluidic Chip with Gap Effect for Manipulation of Oocytes | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610409/ | [
"Shuzhang Liang",
"Satoshi Amaya",
"Hirotaka Sugiura",
"Hao Mo",
"Yuguo Dai",
"Fumihito Arai",
"Shuzhang Liang",
"Satoshi Amaya",
"Hirotaka Sugiura",
"Hao Mo",
"Yuguo Dai",
"Fumihito Arai"
] | This study proposes a novel movable microfluidic chip in which a microfluidic chip is integrated into a robotic manipulator for manipulating oocytes. The microfluidic device has the ability to release a single oocyte with a gap effect. The robotic manipulator can control the position of the microfluidic chip. The microfluidic chip with a pipette tip is directly fabricated using 3D printing. Xenopu... |
Under pressure: learning-based analog gauge reading in the wild | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610793/ | [
"Maurits Reitsma",
"Julian Keller",
"Kenneth Blomqvist",
"Roland Siegwart",
"Maurits Reitsma",
"Julian Keller",
"Kenneth Blomqvist",
"Roland Siegwart"
] | We propose an interpretable framework for reading analog gauges that is deployable on real world robotic systems. Our framework splits the reading task into distinct steps, such that we can detect potential failures at each step. Our system needs no prior knowledge of the type of gauge or the range of the scale and is able to extract the units used. We show that our gauge reading algorithm is able... |
Efficient Composite Learning Robot Control Under Partial Interval Excitation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610877/ | [
"Tian Shi",
"Weibing Li",
"Haoyong Yu",
"Yongping Pan",
"Tian Shi",
"Weibing Li",
"Haoyong Yu",
"Yongping Pan"
] | Parameter convergence in adaptive control is crucial for improving the stability and robustness of robotic systems. Nevertheless, a stringent condition named persistent excitation (PE) needs to be satisfied to ensure parameter convergence in the conventional adaptive robot control. Composite learning robot control (CLRC) is an innovative methodology that guarantees parameter convergence under a co... |
MORALS: Analysis of High-Dimensional Robot Controllers via Topological Tools in a Latent Space | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610383/ | [
"Ewerton R. Vieira",
"Aravind Sivaramakrishnan",
"Sumanth Tangirala",
"Edgar Granados",
"Konstantin Mischaikow",
"Kostas E. Bekris",
"Ewerton R. Vieira",
"Aravind Sivaramakrishnan",
"Sumanth Tangirala",
"Edgar Granados",
"Konstantin Mischaikow",
"Kostas E. Bekris"
] | Estimating the region of attraction (RoA) for a robot controller is essential for safe application and controller composition. Many existing methods require a closed-form expression that limit applicability to data-driven controllers. Methods that operate only over trajectory rollouts tend to be data-hungry. In prior work, we have demonstrated that topological tools based on Morse Graphs (directed... |
Resilient Legged Local Navigation: Learning to Traverse with Compromised Perception End-to-End | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611254/ | [
"Chong Zhang",
"Jin Jin",
"Jonas Frey",
"Nikita Rudin",
"Matías Mattamala",
"Cesar Cadena",
"Marco Hutter",
"Chong Zhang",
"Jin Jin",
"Jonas Frey",
"Nikita Rudin",
"Matías Mattamala",
"Cesar Cadena",
"Marco Hutter"
] | Autonomous robots must navigate reliably in unknown environments even under compromised exteroceptive perception, or perception failures. Such failures often occur when harsh environments lead to degraded sensing, or when the perception algorithm misinterprets the scene due to limited generalization. In this paper, we model perception failures as invisible obstacles and pits, and train a reinforce... |
VLFM: Vision-Language Frontier Maps for Zero-Shot Semantic Navigation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610712/ | [
"Naoki Yokoyama",
"Sehoon Ha",
"Dhruv Batra",
"Jiuguang Wang",
"Bernadette Bucher",
"Naoki Yokoyama",
"Sehoon Ha",
"Dhruv Batra",
"Jiuguang Wang",
"Bernadette Bucher"
] | Understanding how humans leverage semantic knowledge to navigate unfamiliar environments and decide where to explore next is pivotal for developing robots capable of human-like search behaviors. We introduce a zero-shot navigation approach, Vision-Language Frontier Maps (VLFM), which is inspired by human reasoning and designed to navigate towards unseen semantic objects in novel environments. VLFM... |
Learning Continuous Control with Geometric Regularity from Robot Intrinsic Symmetry | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610949/ | [
"Shengchao Yan",
"Baohe Zhang",
"Yuan Zhang",
"Joschka Boedecker",
"Wolfram Burgard",
"Shengchao Yan",
"Baohe Zhang",
"Yuan Zhang",
"Joschka Boedecker",
"Wolfram Burgard"
] | Geometric regularity, which leverages data symmetry, has been successfully incorporated into deep learning architectures such as CNNs, RNNs, GNNs, and Transformers. While this concept has been widely applied in robotics to address the curse of dimensionality when learning from high-dimensional data, the inherent reflectional and rotational symmetry of robot structures has not been adequately explo... |
Learning Vision-Based Bipedal Locomotion for Challenging Terrain | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611621/ | [
"Helei Duan",
"Bikram Pandit",
"Mohitvishnu S. Gadde",
"Bart Van Marum",
"Jeremy Dao",
"Chanho Kim",
"Alan Fern",
"Helei Duan",
"Bikram Pandit",
"Mohitvishnu S. Gadde",
"Bart Van Marum",
"Jeremy Dao",
"Chanho Kim",
"Alan Fern"
] | Reinforcement learning (RL) for bipedal locomotion has recently demonstrated robust gaits over moderate terrains using only proprioceptive sensing. However, such blind controllers will fail in environments where robots must anticipate and adapt to local terrain, which requires visual perception. In this paper, we propose a fully-learned system that allows bipedal robots to react to local terrain w... |
NoMaD: Goal Masked Diffusion Policies for Navigation and Exploration | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610665/ | [
"Ajay Sridhar",
"Dhruv Shah",
"Catherine Glossop",
"Sergey Levine",
"Ajay Sridhar",
"Dhruv Shah",
"Catherine Glossop",
"Sergey Levine"
] | Robotic learning for navigation in unfamiliar environments needs to provide policies for both task-oriented navigation (i.e., reaching a goal that the robot has located), and task-agnostic exploration (i.e., searching for a goal in a novel setting). Typically, these roles are handled by separate models, for example by using subgoal proposals, planning, or separate navigation strategies. In this pa... |
Distributionally Robust Chance Constrained Trajectory Optimization for Mobile Robots within Uncertain Safe Corridor | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611252/ | [
"Shaohang Xu",
"Haolin Ruan",
"Wentao Zhang",
"Yian Wang",
"Lijun Zhu",
"Chin Pang Ho",
"Shaohang Xu",
"Haolin Ruan",
"Wentao Zhang",
"Yian Wang",
"Lijun Zhu",
"Chin Pang Ho"
] | Safe corridor-based Trajectory Optimization (TO) presents an appealing approach for collision-free path planning of autonomous robots, because its convex formulation can guarantee global optimality. The safe corridor is constructed based on the obstacle map, however, the non-ideal perception induces uncertainty, which is rarely considered in the context of trajectory generation. In this paper, we ... |
Distributionally Robust CVaR-Based Safety Filtering for Motion Planning in Uncertain Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611276/ | [
"Sleiman Safaoui",
"Tyler H. Summers",
"Sleiman Safaoui",
"Tyler H. Summers"
] | Safety is a core challenge of autonomous robot motion planning, especially in the presence of dynamic and uncertain obstacles. Many recent results use learning and deep learning-based motion planners and prediction modules to predict multiple possible obstacle trajectories and generate obstacle-aware ego robot plans. However, planners that ignore the inherent uncertainties in such predictions incu... |
Safe POMDP Online Planning via Shielding | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610195/ | [
"Shili Sheng",
"David Parker",
"Lu Feng",
"Shili Sheng",
"David Parker",
"Lu Feng"
] | Partially observable Markov decision processes (POMDPs) have been widely used in many robotic applications for sequential decision-making under uncertainty. POMDP online planning algorithms such as Partially Observable Monte-Carlo Planning (POMCP) can solve very large POMDPs with the goal of maximizing the expected return. But the resulting policies cannot provide safety guarantees which are imper... |
Generating Sparse Probabilistic Graphs for Efficient Planning in Uncertain Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610493/ | [
"Yasmin Veys",
"Martina Stadler Kurtz",
"Nicholas Roy",
"Yasmin Veys",
"Martina Stadler Kurtz",
"Nicholas Roy"
] | Environments with regions of uncertain traversability can be modeled as roadmaps with probabilistic edges for efficient planning under uncertainty. We would like to generate roadmaps that enable planners to efficiently find paths with expected low costs through uncertain environments. The roadmap must be sparse so that the planning problem is tractable, but still contain edges that are likely to c... |
Johnsen-Rahbek Capstan Clutch: A High Torque Electrostatic Clutch | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611283/ | [
"Timothy E. Amish",
"Jeffrey T. Auletta",
"Chad C. Kessens",
"Joshua R. Smith",
"Jeffrey I. Lipton",
"Timothy E. Amish",
"Jeffrey T. Auletta",
"Chad C. Kessens",
"Joshua R. Smith",
"Jeffrey I. Lipton"
] | In many robotic systems, the holding state consumes power, limits operating time, and increases operating costs. Electrostatic clutches have the potential to improve robotic performance by generating holding torques with low power consumption. A key limitation of electrostatic clutches has been their low specific shear stresses which restrict generated holding torque, limiting many applications. H... |
Research on bionic foldable wing for flapping wing micro air vehicle | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610536/ | [
"Shengjie Xiao",
"Kai Hu",
"Yuhong Sun",
"Yun Wang",
"Bo Qin",
"Huichao Deng",
"Xuan Wu",
"Xilun Ding",
"Shengjie Xiao",
"Kai Hu",
"Yuhong Sun",
"Yun Wang",
"Bo Qin",
"Huichao Deng",
"Xuan Wu",
"Xilun Ding"
] | This paper presents a bionic foldable wing that imitates the hind wing of ladybirds. Based on the folding mechanism of the hind wing of ladybirds and the theory of origami, the motion model of the bionic foldable wing is established, yield the motion law of the crease angles and the variation relationship between the panels are obtained. Bionic foldable wings utilise shape memory alloy to drive wi... |
A scalable monolithic 3D printable variable stiffness mechanism | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610379/ | [
"Paul Baisamy",
"A. Stokes",
"F. Giorgio-Serchi",
"Paul Baisamy",
"A. Stokes",
"F. Giorgio-Serchi"
] | Variable Stiffness Mechanisms (VSM) are becoming ubiquitous in mechatronics given the benefit they provide in terms of safety and performance. Despite these assets, VSMs remain fairly complex mechanical devices lacking in compactness, ease of manufacturing and accessibility. In addition, the scarcity of commercially available VSMs requires that such systems are mostly designed in-house. We propose... |
Modular Growing Mechanism with Multi-axis Deformation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610637/ | [
"Dongdong Du",
"Emanuela Del Dottore",
"Alessio Mondini",
"Edoardo Sinibaldi",
"Barbara Mazzolai",
"Dongdong Du",
"Emanuela Del Dottore",
"Alessio Mondini",
"Edoardo Sinibaldi",
"Barbara Mazzolai"
] | Plant cells expand and elongate. Their cumulative actuation defines organ morphing. Inspired by this modular transformability, this study proposes a modular concept for growing robots that will be able to grow by adding at their tip Transformable Modules (TMs). We provide a two-module implementation to evaluate the concept viability. We designed and characterized Shape-Retention Bellows (SRBs) tha... |
Design and Experimental Characterisation of a Novel Quasi-Direct Drive Actuator for Highly Dynamic Robotic Applications | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611567/ | [
"C. Adrián Pérez-Díaz",
"Ignacio Muñoz",
"Daniel Martin-Hernández",
"Carlos Candelo-Zuluaga",
"Ivan Torres",
"Jordi Marsà",
"Daniel Sanz-Merodio",
"Miguel López",
"C. Adrián Pérez-Díaz",
"Ignacio Muñoz",
"Daniel Martin-Hernández",
"Carlos Candelo-Zuluaga",
"Ivan Torres",
"Jordi Marsà",
"Daniel Sanz-Merodio",
"Miguel López"
] | This paper presents the design and experimental results of a proprioceptive, high-bandwidth quasi-direct drive (QDD) actuator for highly dynamic robotic applications. A comprehensive review of the mechanical design of the PULSE115-60 actuator is presented, with particular focus on the design parameters affecting the dynamic performance of the actuator and a full specification is provided. Fundamen... |
Design and Evaluation of a Reconfigurable 7-DOF Upper Limb Rehabilitation Exoskeleton with Gravity Compensation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610011/ | [
"Linliang Zheng",
"Qingcong Wu",
"Yanghui Zhu",
"Qiang Zhang",
"Linliang Zheng",
"Qingcong Wu",
"Yanghui Zhu",
"Qiang Zhang"
] | With the development of society, aging population and the number of stroke patients is increasing year by year. Rehabilitation exoskeleton can help patients to carry out rehabilitation training and improve their activities of daily living (ADL). First of all, a reconfigurable exoskeleton for upper limb rehabilitation is designed in this paper. The exoskeleton combines gravity compensation with lef... |
Flexible Omnidirectional Driving Gear Mechanism with Adaptation over Arbitrary Curvatures | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10609984/ | [
"Moses Gladson Selvamuthu",
"Kazuki Abe",
"Kenjiro Tadakuma",
"Riichiro Tadakuma",
"Moses Gladson Selvamuthu",
"Kazuki Abe",
"Kenjiro Tadakuma",
"Riichiro Tadakuma"
] | A support structure for flexible displays such as OLED or flexible LEDs was developed using the flexible omnidirectional driving gear mechanism. It is a gear mechanism having two degrees of freedom on one surface. This flexible display mechanism is expected to be placed inside a car dashboard as a human interface and for workspace optimization. In this study, we propose a novel flexible omnidirect... |
Tactile Robot Programming: Transferring Task Constraints into Constraint-Based Unified Force-Impedance Control | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610054/ | [
"Kübra Karacan",
"Robin Jeanne Kirschner",
"Hamid Sadeghian",
"Fan Wu",
"Sami Haddadin",
"Kübra Karacan",
"Robin Jeanne Kirschner",
"Hamid Sadeghian",
"Fan Wu",
"Sami Haddadin"
] | Flexible manufacturing lines are required to meet the demand for customized and small batch-size products. Even though state-of-the-art tactile robots may provide the versatility for increased adaptability and flexibility, their potential is yet to be fully exploited. To support robotics deployment in manufacturing, we propose a task-based tactile robot programming paradigm that uses an object-cen... |
Safety Verification of Closed-loop Control System with Anytime Perception | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611044/ | [
"Lipsy Gupta",
"Jahid Chowdhury Choton",
"Pavithra Prabhakar",
"Lipsy Gupta",
"Jahid Chowdhury Choton",
"Pavithra Prabhakar"
] | In this paper, we consider the problem of safety analysis of a closed-loop control system with anytime perception sensor. We formalize the framework and present a general procedure for safety analysis using reachable set computation. We instantiate the procedure for two concrete classes, namely, the classical discrete-time linear system with linear state feedback controller and an extension with v... |
Unraveling the Single Tangent Space Fallacy: An Analysis and Clarification for Applying Riemannian Geometry in Robot Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611701/ | [
"Noémie Jaquier",
"Leonel Rozo",
"Tamim Asfour",
"Noémie Jaquier",
"Leonel Rozo",
"Tamim Asfour"
] | In the realm of robotics, numerous downstream robotics tasks leverage machine learning methods for processing, modeling, or synthesizing data. Often, this data comprises variables that inherently carry geometric constraints, such as the unit-norm condition of quaternions representing rigid-body orientations or the positive definiteness of stiffness and manipulability ellipsoids. Handling such geom... |
Optimal Control Synthesis with Relaxed Global Temporal Logic Specifications for Homogeneous Multi-robot Teams | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610142/ | [
"Disha Kamale",
"Cristian-Ioan Vasile",
"Disha Kamale",
"Cristian-Ioan Vasile"
] | In this work, we address the problem of control synthesis for a homogeneous team of robots given a global temporal logic specification and formal user preferences for relaxation in case of infeasibility. The relaxation preferences are represented as a Weighted Finite-state Edit System and are used to compute a relaxed specification automaton that captures all allowable relaxations of the mission s... |
An Iterative Approach for Heterogeneous Multi-Agent Route Planning with Temporal Logic Goals and Travel Duration Uncertainty | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611519/ | [
"Kaier Liang",
"Gustavo A. Cardona",
"Cristian-Ioan Vasile",
"Kaier Liang",
"Gustavo A. Cardona",
"Cristian-Ioan Vasile"
] | This paper introduces an iterative approach to multi-agent route planning under chance constraints. A heterogeneous team of agents with various capabilities is tasked with a Capability Temporal Logic (CaTL) mission, a fragment of Signal Temporal Logic. The agents’ motion is modeled as a finite weighted graph, where the weights represent travel durations. Given the probability distribution over the... |
Phasic Diversity Optimization for Population-Based Reinforcement Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610814/ | [
"Jingcheng Jiang",
"Haiyin Piao",
"Yu Fu",
"Yihang Hao",
"Chuanlu Jiang",
"Ziqi Wei",
"Xin Yang",
"Jingcheng Jiang",
"Haiyin Piao",
"Yu Fu",
"Yihang Hao",
"Chuanlu Jiang",
"Ziqi Wei",
"Xin Yang"
] | Reviewing the previous work of diversity Reinforcement Learning, diversity is often obtained via an augmented loss function, which requires a balance between reward and diversity. Generally, diversity optimization algorithms use Multi-armed Bandits algorithms to select the coefficient in the pre-defined space. However, the dynamic distribution of reward signals for MABs or the conflict between qua... |
VO-Safe Reinforcement Learning for Drone Navigation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611487/ | [
"Feiqiang Lin",
"Changyun Wei",
"Raphael Grech",
"Ze Ji",
"Feiqiang Lin",
"Changyun Wei",
"Raphael Grech",
"Ze Ji"
] | This work is focused on reinforcement learning (RL)-based navigation for drones, whose localisation is based on visual odometry (VO). Such drones should avoid flying into areas with poor visual features, as this can lead to deteriorated localization or complete loss of tracking. To achieve this, we propose a hierarchical control scheme, which uses an RL-trained policy as the high-level controller ... |
RoCo: Dialectic Multi-Robot Collaboration with Large Language Models | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610855/ | [
"Zhao Mandi",
"Shreeya Jain",
"Shuran Song",
"Zhao Mandi",
"Shreeya Jain",
"Shuran Song"
] | We propose a novel approach to multi-robot collaboration that harnesses the power of pre-trained large language models (LLMs) for both high-level communication and low-level path planning. Robots are equipped with LLMs to discuss and collectively reason task strategies. They generate sub-task plans and task space waypoint paths, which are used by a multi-arm motion planner to accelerate trajectory... |
Collision Avoidance and Navigation for a Quadrotor Swarm Using End-to-end Deep Reinforcement Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611499/ | [
"Zhehui Huang",
"Zhaojing Yang",
"Rahul Krupani",
"Baskın Şenbaşlar",
"Sumeet Batra",
"Gaurav S. Sukhatme",
"Zhehui Huang",
"Zhaojing Yang",
"Rahul Krupani",
"Baskın Şenbaşlar",
"Sumeet Batra",
"Gaurav S. Sukhatme"
] | End-to-end deep reinforcement learning (DRL) for quadrotor control promises many benefits – easy deployment, task generalization and real-time execution capability. Prior end-to-end DRL-based methods have showcased the ability to deploy learned controllers onto single quadrotors or quadrotor teams maneuvering in simple, obstacle-free environments. However, the addition of obstacles increases the n... |
Multi-Level Action Tree Rollout (MLAT-R): Efficient and Accurate Online Multiagent Policy Improvement | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610888/ | [
"Andrea Henshall",
"Sertac Karaman",
"Andrea Henshall",
"Sertac Karaman"
] | Rollout algorithms are renowned for their abilities to correct for the suboptimalities of offline-trained base policies. In the multiagent setting, performing online rollout can require an exponentially large number of optimizations with respect to the number of agents. One-agent-at-a-time algorithms offer computationally efficient approaches to guaranteed policy improvement; however, this improve... |
Stimulate the Potential of Robots via Competition | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611581/ | [
"Kangyao Huang",
"Di Guo",
"Xinyu Zhang",
"Xiangyang Ji",
"Huaping Liu",
"Kangyao Huang",
"Di Guo",
"Xinyu Zhang",
"Xiangyang Ji",
"Huaping Liu"
] | It is common for us to feel pressure in a competition environment, which arises from the desire to obtain success comparing with other individuals or opponents. Although we might get anxious under the pressure, it could also be a drive for us to stimulate our potentials to the best in order to keep up with others. Inspired by this, we propose a competitive learning framework which is able to help ... |
Multi-modal 3D Human Tracking for Robots in Complex Environment with Siamese Point-Video Transformer | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610979/ | [
"Shuo Xin",
"Zhen Zhang",
"Mengmeng Wang",
"Xiaojun Hou",
"Yaowei Guo",
"Xiao Kang",
"Liang Liu",
"Yong Liu",
"Shuo Xin",
"Zhen Zhang",
"Mengmeng Wang",
"Xiaojun Hou",
"Yaowei Guo",
"Xiao Kang",
"Liang Liu",
"Yong Liu"
] | Tracking a specific person in 3D scene is gaining momentum due to its numerous applications in robotics. Currently, most 3D trackers focus on driving scenarios with neglected jitter and uncomplicated surroundings, which results in their severe degeneration in complex environments, especially on jolting robot platforms (only 20-60% success rate). To improve the accuracy, a Point-Video-based Transfo... |
Efficient Gesture Recognition on Spiking Convolutional Networks Through Sensor Fusion of Event-Based and Depth Data | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610824/ | [
"Lea Steffen",
"Thomas Trapp",
"Arne Roennau",
"Rüdiger Dillmann",
"Lea Steffen",
"Thomas Trapp",
"Arne Roennau",
"Rüdiger Dillmann"
] | As intelligent systems become increasingly important in our daily lives, new ways of interaction are needed. Classical user interfaces pose issues for the physically impaired and are partially not practical or convenient. Gesture recognition is an alternative, but often not reactive enough when conventional cameras are used. This work proposes a Spiking Convolutional Neural Network, processing eve... |
Point Cloud-Based Control Barrier Function Regression for Safe and Efficient Vision-Based Control | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610647/ | [
"Massimiliano De Sa",
"Prasanth Kotaru",
"Koushil Sreenath",
"Massimiliano De Sa",
"Prasanth Kotaru",
"Koushil Sreenath"
] | Control barrier functions have become an increasingly popular framework for safe real-time control. In this work, we present a computationally low-cost framework for synthesizing barrier functions over point cloud data for safe vision-based control. We take advantage of surface geometry to locally define and synthesize a quadratic CBF over a point cloud. This CBF is used in a CBF-QP for control an... |
An Image Acquisition Scheme for Visual Odometry based on Image Bracketing and Online Attribute Control | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611141/ | [
"Shuyang Zhang",
"Jinhao He",
"Bohuan Xue",
"Jin Wu",
"Pengyu Yin",
"Jianhao Jiao",
"Ming Liu",
"Shuyang Zhang",
"Jinhao He",
"Bohuan Xue",
"Jin Wu",
"Pengyu Yin",
"Jianhao Jiao",
"Ming Liu"
] | Visual odometry (VO) system is challenged by complex illumination environments. Image quality and its consistency in the time domain directly determine feature detection and tracking performance, which further affect the robustness and accuracy of the entire system. In this paper, an image acquisition scheme with image bracketing patterns is proposed. Images with different exposure levels are cont... |
MagicTac: A Novel High-Resolution 3D Multi-layer Grid-Based Tactile Sensor | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610615/ | [
"Wen Fan",
"Haoran Li",
"Dandan Zhang",
"Wen Fan",
"Haoran Li",
"Dandan Zhang"
] | Accurate robotic control over interactions with the environment is fundamentally grounded in understanding tactile contacts. In this paper, we introduce MagicTac, a novel high-resolution grid-based tactile sensor. This sensor employs a 3D multi-layer grid-based design, inspired by the Magic Cube structure. This structure can help increase the spatial resolution of MagicTac to perceive external int... |
Mobile Bot Rotation Using Sound Source Localization And Distant Speech Recognition | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610539/ | [
"Swapnil Sontakke",
"Pradyoth Hegde",
"Prashant Bannulmath",
"Deepak K T",
"Swapnil Sontakke",
"Pradyoth Hegde",
"Prashant Bannulmath",
"Deepak K T"
] | In the last few years, mobile robots such as floor cleaners, assistive robots, and home telepresence have become an essential part of our day-to-day activities. In human-robot interaction, speech is the preferred way of communication, especially in indoor environments. This paper proposes a speech module to rotate the mobile robot. It has two components, namely, a distant automatic speech recogniz... |
Diving into the Depths of Spotting Text in Multi-Domain Noisy Scenes | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611120/ | [
"Alloy Das",
"Sanket Biswas",
"Umapada Pal",
"Josep Lladós",
"Alloy Das",
"Sanket Biswas",
"Umapada Pal",
"Josep Lladós"
] | When used in a real-world noisy environment, the capacity to generalize to multiple domains is essential for any autonomous scene text spotting system. However, existing state-of-the-art methods employ pretraining and fine-tuning strategies on natural scene datasets, which do not exploit the feature interaction across other complex domains. In this work, we explore and investigate the problem of d... |
Masked Local-Global Representation Learning for 3D Point Cloud Domain Adaptation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611402/ | [
"Bowei Xing",
"Xianghua Ying",
"Ruibin Wang",
"Bowei Xing",
"Xianghua Ying",
"Ruibin Wang"
] | Point cloud is a popular and widely used geometric representation, which has attracted significant attention in 3D vision. However, the geometric variability of point cloud representations across different datasets can cause domain discrepancies, which hinder knowledge transfer and model generalization, resulting in degraded performance in target domain. In this paper, we present a novel approach ... |
Continuous Adaptation in Person Re-identification for Robotic Assistance | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611226/ | [
"Federico Rollo",
"Andrea Zunino",
"Nikolaos Tsagarakis",
"Enrico Mingo Hoffman",
"Arash Ajoudani",
"Federico Rollo",
"Andrea Zunino",
"Nikolaos Tsagarakis",
"Enrico Mingo Hoffman",
"Arash Ajoudani"
] | In scenarios of Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), it is often assumed that the robot should cooperate with the closest individual or that only one person is present. However, in real-life situations, such as shop floor operations, this assumption may not hold. Thus, it becomes necessary for a robot to recognize a specific target in a crowded environment. To address this problem, we propose a person r... |
Incorporating Scene Graphs into Pre-trained Vision-Language Models for Multimodal Open-vocabulary Action Recognition | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611454/ | [
"Chao Wei",
"Zhidong Deng",
"Chao Wei",
"Zhidong Deng"
] | This paper presents Action-SGFA, a novel action feature alignment approach to learn unified joint embeddings across four action modalities incorporating scene graph (SG) comprehension. A new training paradigm for Action-SGFA is also devised to improve pre-trained VL models using datasets with SG annotation. When learning from image-SG pairs, it captures structure-associated action knowledge for vi... |
LPS-Net: Lightweight Parameter-shared Network for Point Cloud-based Place Recognition | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610758/ | [
"Chengxin Liu",
"Guiyou Chen",
"Ran Song",
"Chengxin Liu",
"Guiyou Chen",
"Ran Song"
] | With innovation in fields such as autonomous driving and augmented reality, point cloud-based place recognition has gained significant attention. Many methods try to address this problem by extracting and matching global descriptors in a database, but they often must balance the extraction of comprehensive contextual information and large model sizes. To overcome this challenge, we propose a light... |
Joint Response and Background Learning for UAV Visual Tracking | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611308/ | [
"Biao Wang",
"Wenling Li",
"Bin Zhang",
"Yang Liu",
"Biao Wang",
"Wenling Li",
"Bin Zhang",
"Yang Liu"
] | Correlation filter (CF)-based approaches have gained widespread attention in the field of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) visual tracking due to their light-weight characteristics. However, CFs are prone to generating low-quality response in challenging UAV scenarios, e.g., fast motion and background clutter. In this paper, in order to model the tracker more robustly, we first conduct an effective r... |
ZS6D: Zero-shot 6D Object Pose Estimation using Vision Transformers | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611464/ | [
"Philipp Ausserlechner",
"David Haberger",
"Stefan Thalhammer",
"Jean-Baptiste Weibel",
"Markus Vincze",
"Philipp Ausserlechner",
"David Haberger",
"Stefan Thalhammer",
"Jean-Baptiste Weibel",
"Markus Vincze"
] | As robotic systems increasingly encounter complex and unconstrained real-world scenarios, there is a demand to recognize diverse objects. The state-of-the-art 6D object pose estimation methods rely on object-specific training and therefore do not generalize to unseen objects. Recent novel object pose estimation methods are solving this issue using task-specific fine-tuned CNNs for deep template ma... |
VERSE: Virtual-Gradient Aware Streaming Lifelong Learning with Anytime Inference | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610702/ | [
"Soumya Banerjee",
"Vinay K. Verma",
"Avideep Mukherjee",
"Deepak Gupta",
"Vinay P. Namboodiri",
"Piyush Rai",
"Soumya Banerjee",
"Vinay K. Verma",
"Avideep Mukherjee",
"Deepak Gupta",
"Vinay P. Namboodiri",
"Piyush Rai"
] | Lifelong learning or continual learning is the problem of training an AI agent continuously while also preventing it from forgetting its previously acquired knowledge. Streaming lifelong learning is a challenging setting of lifelong learning with the goal of continuous learning in a dynamic non-stationary environment without forgetting. We introduce a novel approach to lifelong learning, which is ... |
Experience Consistency Distillation Continual Reinforcement Learning for Robotic Manipulation Tasks | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611494/ | [
"Chao Zhao",
"Jie Xu",
"Ru Peng",
"Xingyu Chen",
"Kuizhi Mei",
"Xuguang Lan",
"Chao Zhao",
"Jie Xu",
"Ru Peng",
"Xingyu Chen",
"Kuizhi Mei",
"Xuguang Lan"
] | Continual reinforcement learning, which aims to help robots acquire skills without catastrophic forgetting, obviating the need to re-learn all tasks from scratch. In order to enable lifelong acquisition of skills in robots, replay-based continual reinforcement learning has emerged as a promising research direction. These techniques replay data from previous tasks to mitigate forgetting when learni... |
Adapting to the “Open World”: The Utility of Hybrid Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning and Symbolic Planning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611594/ | [
"Pierrick Lorang",
"Helmut Horvath",
"Tobias Kietreiber",
"Patrik Zips",
"Clemens Heitzinger",
"Matthias Scheutz",
"Pierrick Lorang",
"Helmut Horvath",
"Tobias Kietreiber",
"Patrik Zips",
"Clemens Heitzinger",
"Matthias Scheutz"
] | Open-world robotic tasks such as autonomous driving pose significant challenges to robot control due to unknown and unpredictable events that disrupt task performance. Neural network-based reinforcement learning (RL) techniques (like DQN, PPO, SAC, etc.) struggle to adapt in large domains and suffer from catastrophic forgetting. Hybrid planning and RL approaches have shown some promise in handling... |
Lifelong Robot Library Learning: Bootstrapping Composable and Generalizable Skills for Embodied Control with Language Models | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611448/ | [
"Georgios Tziafas",
"Hamidreza Kasaei",
"Georgios Tziafas",
"Hamidreza Kasaei"
] | Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as a new paradigm for embodied reasoning and control, most recently by generating robot policy code that utilizes a custom library of vision and control primitive skills. However, prior arts fix their skills library and steer the LLM with carefully handcrafted prompt engineering, limiting the agent to a stationary range of addressable tasks. In this work, ... |
Lifelong Robot Learning with Human Assisted Language Planners | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610225/ | [
"Meenal Parakh",
"Alisha Fong",
"Anthony Simeonov",
"Tao Chen",
"Abhishek Gupta",
"Pulkit Agrawal",
"Meenal Parakh",
"Alisha Fong",
"Anthony Simeonov",
"Tao Chen",
"Abhishek Gupta",
"Pulkit Agrawal"
] | Large Language Models (LLMs) have been shown to act like planners that can decompose high-level instructions into a sequence of executable instructions. However, current LLM-based planners are only able to operate with a fixed set of skills. We overcome this critical limitation and present a method for using LLM-based planners to query new skills and teach robots these skills in a data and time-ef... |
Probabilistic Spiking Neural Network for Robotic Tactile Continual Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610553/ | [
"Senlin Fang",
"Yiwen Liu",
"Chengliang Liu",
"Jingnan Wang",
"Yuanzhe Su",
"Yupo Zhang",
"Hoiio Kong",
"Zhengkun Yi",
"Xinyu Wu",
"Senlin Fang",
"Yiwen Liu",
"Chengliang Liu",
"Jingnan Wang",
"Yuanzhe Su",
"Yupo Zhang",
"Hoiio Kong",
"Zhengkun Yi",
"Xinyu Wu"
] | The sense of touch is essential for robots to perform various daily tasks. Artificial Neural Networks have shown significant promise in advancing robotic tactile learning. However, due to the changing of tactile data distribution as robots encounter new tasks, ANN-based robotic tactile learning suffers from catastrophic forgetting. To solve this problem, we introduce a novel continual learning (CL... |
LOTUS: Continual Imitation Learning for Robot Manipulation Through Unsupervised Skill Discovery | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611129/ | [
"Weikang Wan",
"Yifeng Zhu",
"Rutav Shah",
"Yuke Zhu",
"Weikang Wan",
"Yifeng Zhu",
"Rutav Shah",
"Yuke Zhu"
] | We introduce LOTUS, a continual imitation learning algorithm that empowers a physical robot to continuously and efficiently learn to solve new manipulation tasks throughout its lifespan. The core idea behind LOTUS is constructing an ever-growing skill library from a sequence of new tasks with a small number of human demonstrations. LOTUS starts with a continual skill discovery process using an ope... |
Synthesize Efficient Safety Certificates for Learning-Based Safe Control using Magnitude Regularization | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610959/ | [
"Haotian Zheng",
"Haitong Ma",
"Sifa Zheng",
"Shengbo Eben Li",
"Jianqiang Wang",
"Haotian Zheng",
"Haitong Ma",
"Sifa Zheng",
"Shengbo Eben Li",
"Jianqiang Wang"
] | Safety certificates based on energy functions can provide demonstrable safety for complex robotic systems. However, all recent studies on learning-based energy function synthesis only consider the feasibility of the control policy, which might cause over-conservativeness and even fail to achieve the control goal. To solve the problem of over-conservative controllers, we proposed the magnitude regu... |
GG-LLM: Geometrically Grounding Large Language Models for Zero-shot Human Activity Forecasting in Human-Aware Task Planning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611090/ | [
"Moritz A. Graule",
"Volkan Isler",
"Moritz A. Graule",
"Volkan Isler"
] | A robot in a human-centric environment needs to account for the human’s intent and future motion in its task and motion planning to ensure safe and effective operation. This requires symbolic reasoning about probable future actions and the ability to tie these actions to specific locations in the physical environment. While one can train behavioral models capable of predicting human motion from pa... |
Adaptive Whole-body Robotic Tool-use Learning on Low-rigidity Plastic-made Humanoids Using Vision and Tactile Sensors | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610913/ | [
"Kento Kawaharazuka",
"Kei Okada",
"Masayuki Inaba",
"Kento Kawaharazuka",
"Kei Okada",
"Masayuki Inaba"
] | Various robots have been developed so far; however, we face challenges in modeling the low-rigidity bodies of some robots. In particular, the deflection of the body changes during tool-use due to object grasping, resulting in significant shifts in the tool-tip position and the body’s center of gravity. Moreover, this deflection varies depending on the weight and length of the tool, making these mo... |
Robotic Constrained Imitation Learning for the Peg Transfer Task in Fundamentals of Laparoscopic Surgery | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610059/ | [
"Kento Kawaharazuka",
"Kei Okada",
"Masayuki Inaba",
"Kento Kawaharazuka",
"Kei Okada",
"Masayuki Inaba"
] | In this study, we present an implementation strategy for a robot that performs peg transfer tasks in Fundamentals of Laparoscopic Surgery (FLS) via imitation learning, aimed at the development of an autonomous robot for laparoscopic surgery. Robotic laparoscopic surgery presents two main challenges: (1) the need to manipulate forceps using ports established on the body surface as fulcrums, and (2)... |
Mobile Robot Oriented Large-Scale Indoor Dataset for Dynamic Scene Understanding | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611489/ | [
"Yi-Fan Tang",
"Cong Tai",
"Fang-Xing Chen",
"Wan-Ting Zhang",
"Tao Zhang",
"Xue-Ping Liu",
"Yong-Jin Liu",
"Long Zeng",
"Yi-Fan Tang",
"Cong Tai",
"Fang-Xing Chen",
"Wan-Ting Zhang",
"Tao Zhang",
"Xue-Ping Liu",
"Yong-Jin Liu",
"Long Zeng"
] | Most existing robotic datasets capture static scene data and thus are limited in evaluating robots’ dynamic performance. To address this, we present a mobile robot oriented large-scale indoor dataset, denoted as THUD (Tsinghua University Dynamic) robotic dataset, for training and evaluating their dynamic scene understanding algorithms. Specifically, the THUD dataset construction is first detailed,... |
InteRACT: Transformer Models for Human Intent Prediction Conditioned on Robot Actions | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610681/ | [
"Kushal Kedia",
"Atiksh Bhardwaj",
"Prithwish Dan",
"Sanjiban Choudhury",
"Kushal Kedia",
"Atiksh Bhardwaj",
"Prithwish Dan",
"Sanjiban Choudhury"
] | In collaborative human-robot manipulation, a robot must predict human intents and adapt its actions accordingly to smoothly execute tasks. However, the human’s intent in turn depends on actions the robot takes, creating a chicken-or-egg problem. Prior methods ignore such inter-dependency and instead train marginal intent prediction models independent of robot actions. This is because training cond... |
Towards learning-based planning: The nuPlan benchmark for real-world autonomous driving | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610077/ | [
"Napat Karnchanachari",
"Dimitris Geromichalos",
"Kok Seang Tan",
"Nanxiang Li",
"Christopher Eriksen",
"Shakiba Yaghoubi",
"Noushin Mehdipour",
"Gianmarco Bernasconi",
"Whye Kit Fong",
"Yiluan Guo",
"Holger Caesar",
"Napat Karnchanachari",
"Dimitris Geromichalos",
"Kok Seang Tan",
"Nanxiang Li",
"Christopher Eriksen",
"Shakiba Yaghoubi",
"Noushin Mehdipour",
"Gianmarco Bernasconi",
"Whye Kit Fong",
"Yiluan Guo",
"Holger Caesar"
] | Machine Learning (ML) has replaced handcrafted methods for perception and prediction in autonomous vehicles. Yet for the equally important planning task, the adoption of ML-based techniques is slow. We present nuPlan, the world’s first real-world autonomous driving dataset and benchmark. The benchmark is designed to test the ability of ML-based planners to handle diverse driving situations and to ... |
TBD Pedestrian Data Collection: Towards Rich, Portable, and Large-Scale Natural Pedestrian Data | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610335/ | [
"Allan Wang",
"Daisuke Sato",
"Yasser Corzo",
"Sonya Simkin",
"Abhijat Biswas",
"Aaron Steinfeld",
"Allan Wang",
"Daisuke Sato",
"Yasser Corzo",
"Sonya Simkin",
"Abhijat Biswas",
"Aaron Steinfeld"
] | Social navigation and pedestrian behavior research has shifted towards machine learning-based methods and converged on the topic of modeling inter-pedestrian interactions and pedestrian-robot interactions. For this, large-scale datasets that contain rich information are needed. We describe a portable data collection system, coupled with a semi-autonomous labeling pipeline. As part of the pipeline,... |
RoboVQA: Multimodal Long-Horizon Reasoning for Robotics | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610216/ | [
"Pierre Sermanet",
"Tianli Ding",
"Jeffrey Zhao",
"Fei Xia",
"Debidatta Dwibedi",
"Keerthana Gopalakrishnan",
"Christine Chan",
"Gabriel Dulac-Arnold",
"Sharath Maddineni",
"Nikhil J Joshi",
"Pete Florence",
"Wei Han",
"Robert Baruch",
"Yao Lu",
"Suvir Mirchandani",
"Peng Xu",
"Pannag Sanketi",
"Karol Hausman",
"Izhak Shafran",
"Brian Ichter",
"Yuan Cao",
"Pierre Sermanet",
"Tianli Ding",
"Jeffrey Zhao",
"Fei Xia",
"Debidatta Dwibedi",
"Keerthana Gopalakrishnan",
"Christine Chan",
"Gabriel Dulac-Arnold",
"Sharath Maddineni",
"Nikhil J Joshi",
"Pete Florence",
"Wei Han",
"Robert Baruch",
"Yao Lu",
"Suvir Mirchandani",
"Peng Xu",
"Pannag Sanketi",
"Karol Hausman",
"Izhak Shafran",
"Brian Ichter",
"Yuan Cao"
] | We present a scalable, bottom-up and intrinsically diverse data collection scheme that can be used for high-level reasoning with long and medium horizons and that has 2.2x higher throughput compared to traditional narrow top-down step-by-step collection. We collect realistic data by performing any user requests within the entirety of 3 office buildings and using multiple embodiments (robot, human,... |
RH20T: A Comprehensive Robotic Dataset for Learning Diverse Skills in One-Shot | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611615/ | [
"Hao-Shu Fang",
"Hongjie Fang",
"Zhenyu Tang",
"Jirong Liu",
"Chenxi Wang",
"Junbo Wang",
"Haoyi Zhu",
"Cewu Lu",
"Hao-Shu Fang",
"Hongjie Fang",
"Zhenyu Tang",
"Jirong Liu",
"Chenxi Wang",
"Junbo Wang",
"Haoyi Zhu",
"Cewu Lu"
] | A key challenge for robotic manipulation in open domains is how to acquire diverse and generalizable skills for robots. Recent progress in one-shot imitation learning and robotic foundation models have shown promise in transferring trained policies to new tasks based on demonstrations. This feature is attractive for enabling robots to acquire new skills and improve their manipulative ability. Howe... |
Lightweight Untethered Soft Robotic Fish | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610533/ | [
"Xiangxing Wang",
"Xuan Pei",
"Xinyang Wang",
"Taogang Hou",
"Xiangxing Wang",
"Xuan Pei",
"Xinyang Wang",
"Taogang Hou"
] | Aquatic organisms, due to soft body structure and high agility, have inspired many biomimetic robots. However, considering the issues of insulation and waterproofing, as well as the driving module of soft materials, their control systems are usually larger and heavier. Therefore, small underwater robots often tethered, i.e., it cannot integrate energy and control systems onto the body, which great... |
A scalable, light-controlled, individually addressable, non-metal actuator array | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610023/ | [
"Sophie Paul",
"Matthew R. Devlin",
"Elliot W. Hawkes",
"Sophie Paul",
"Matthew R. Devlin",
"Elliot W. Hawkes"
] | Research in the area of photo-actuation is growing rapidly, yet there are few examples of photo-actuators with practical use cases. One potential application is for the control of intelligent electromagnetic surfaces, or two-dimensional arrays that could shape and control an incident electromagnetic field in ideally any manner. A promising concept to realize such a surface leverages signal refract... |
A Passively Bendable, Compliant Tactile Palm with RObotic Modular Endoskeleton Optical (ROMEO) Fingers | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611043/ | [
"Sandra Q. Liu",
"Edward H. Adelson",
"Sandra Q. Liu",
"Edward H. Adelson"
] | Many robotic hands currently rely on extremely dexterous robotic fingers and a thumb joint to envelop themselves around an object. Few hands focus on the palm even though human hands greatly benefit from their central fold and soft surface. As such, we develop a novel structurally compliant soft palm, which enables more surface area contact for the objects that are pressed into it. Moreover, this ... |
A Phase-Change Emulsion Jamming Gripper for Manipulation of Micro-Scale Textured Surfaces | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611273/ | [
"Alex Keller",
"Tianqi Yue",
"Qiukai Qi",
"Andrew T. Conn",
"Jonathan Rossiter",
"Alex Keller",
"Tianqi Yue",
"Qiukai Qi",
"Andrew T. Conn",
"Jonathan Rossiter"
] | The inherent elasticity of soft materials can be used to create robotic grippers that deform and comply to a variety of irregular shapes. To date, several soft adaptive grasping strategies have been reported, however, most of them focus on adapting to the overall shape of the structure, while the adaptive grasping of small surface asperities is overlooked. In this paper, we propose a novel method ... |
Design and Fabrication of String-driven Origami Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610989/ | [
"Peiwen Yang",
"Shuguang Li",
"Peiwen Yang",
"Shuguang Li"
] | Origami designs and structures have been widely used in many fields, such as morphing structures, robotics, and metamaterials. However, the design and fabrication of origami structures rely on human experiences and skills, which are both time and labor-consuming. In this paper, we present a rapid design and fabrication method for string-driven origami structures and robots. We developed an origami... |
Multi-Confidence Guided Source-Free Domain Adaption Method for Point Cloud Primitive Segmentation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611600/ | [
"Shaohu Wang",
"Yuchuang Tong",
"Xiuqin Shang",
"Zhengtao Zhang",
"Shaohu Wang",
"Yuchuang Tong",
"Xiuqin Shang",
"Zhengtao Zhang"
] | Point cloud primitive segmentation aims to segment the surface point cloud into various geometric types of primitives, which plays a vital role in robot operation and industrial automation. However, differences in object structures and shapes across industrial datasets create domain shift issues, compounded by privacy concerns preventing dataset sharing. To address these challenges, we propose a n... |
FF-LOGO: Cross-Modality Point Cloud Registration with Feature Filtering and Local to Global Optimization | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610549/ | [
"Nan Ma",
"Mohan Wang",
"Yiheng Han",
"Yong-Jin Liu",
"Nan Ma",
"Mohan Wang",
"Yiheng Han",
"Yong-Jin Liu"
] | Cross-modality point cloud registration is confronted with significant challenges due to inherent differences in modalities between sensors. To deal with this problem, we propose FF-LOGO: a cross-modality point cloud registration framework with Feature Filtering and LOcal-Global Optimization. The cross-modality feature correlation filtering module extracts geometric transformation-invariant featur... |
CAPT: Category-level Articulation Estimation from a Single Point Cloud Using Transformer | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611073/ | [
"Lian Fu",
"Ryoichi Ishikawa",
"Yoshihiro Sato",
"Takeshi Oishi",
"Lian Fu",
"Ryoichi Ishikawa",
"Yoshihiro Sato",
"Takeshi Oishi"
] | The ability to estimate joint parameters is essential for various applications in robotics and computer vision. In this paper, we propose CAPT: category-level articulation estimation from a point cloud using Transformer. CAPT uses an end-to-end transformer-based architecture for joint parameter and state estimation of articulated objects from a single point cloud. The proposed CAPT methods accurat... |
EdgePoint: Efficient Point Detection and Compact Description via Distillation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611607/ | [
"Haodi Yao",
"Ning Hao",
"Chen Xie",
"Fenghua He",
"Haodi Yao",
"Ning Hao",
"Chen Xie",
"Fenghua He"
] | Efficient interest point detection and description in images play a crucial role in many tasks such as multi-robot SLAM and collaborative localization. To facilitate fast detection and generate compact descriptions on edge devices, we introduce EdgePoint, a lightweight neural network. We design a new detection loss UnfoldSoftmax to improve inference speed. Futhermore, we propose Ortho-Alignment lo... |
Fast and Robust Point Cloud Registration with Tree-based Transformer | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610004/ | [
"Guangyan Chen",
"Meiling Wang",
"Yi Yang",
"Li Yuan",
"Yufeng Yue",
"Guangyan Chen",
"Meiling Wang",
"Yi Yang",
"Li Yuan",
"Yufeng Yue"
] | Point cloud registration is essential in computer vision and robotics. Recently, transformer-based methods have achieved advanced point cloud registration performance. However, the standard attention mechanism utilized in these methods considers many low-relevance points, and it has difficulty focusing its attention weights on sparse and meaningful points, leading to limited local structure modeli... |
Uncertainty-driven Exploration Strategies for Online Grasp Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610056/ | [
"Yitian Shi",
"Philipp Schillinger",
"Miroslav Gabriel",
"Alexander Qualmann",
"Zohar Feldman",
"Hanna Ziesche",
"Ngo Anh Vien",
"Yitian Shi",
"Philipp Schillinger",
"Miroslav Gabriel",
"Alexander Qualmann",
"Zohar Feldman",
"Hanna Ziesche",
"Ngo Anh Vien"
] | Existing grasp prediction approaches are mostly based on offline learning, while, ignoring the exploratory grasp learning during online adaptation to new picking scenarios, i.e., objects that are unseen or out-of-domain (OOD), camera and bin settings, etc. In this paper, we present an uncertainty-based approach for online learning of grasp predictions for robotic bin picking. Specifically, the onl... |
Pseudo Labeling and Contextual Curriculum Learning for Online Grasp Learning in Robotic Bin Picking | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611348/ | [
"Huy Le",
"Philipp Schillinger",
"Miroslav Gabriel",
"Alexander Qualmann",
"Ngo Anh Vien",
"Huy Le",
"Philipp Schillinger",
"Miroslav Gabriel",
"Alexander Qualmann",
"Ngo Anh Vien"
] | The prevailing grasp prediction methods predominantly rely on offline learning, overlooking the dynamic grasp learning that occurs during real-time adaptation to novel picking scenarios. These scenarios may involve previously unseen objects, variations in camera perspectives, and bin configurations, among other factors. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach, SSL-ConvSAC, that combines semi-... |
PoseFusion: Multi-Scale Keypoint Correspondence for Monocular Camera-to-Robot Pose Estimation in Robotic Manipulation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610844/ | [
"Xujun Han",
"Shaochen Wang",
"Xiucai Huang",
"Zhen Kan",
"Xujun Han",
"Shaochen Wang",
"Xiucai Huang",
"Zhen Kan"
] | Visual-based robot pose estimation is a fundamental challenge, involving the determination of the camera’s pose with respect to a robot. Conventional methods for camera-to-robot pose calibration rely on fiducial markers to establish keypoint correspondences. However, these approaches exhibit significant variability in accuracy and robustness, particularly in 2D keypoint detection. In this work, we... |
Online Fault Detection in Manipulation Tasks via Generative Models | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611418/ | [
"Michael W. Lanighan",
"Oscar Youngquist",
"Michael W. Lanighan",
"Oscar Youngquist"
] | This paper introduces a method, Generative Adversarial Networks for Detecting Erroneous Results (GANDER), leveraging Generative Adversarial Networks to provide online error detection in manipulation tasks for autonomous robot systems. GANDER relies on mapping input images of a trained task to a learned manifold that contains only positive task executions and outcomes. When reconstructed through th... |
Multi-level Reasoning for Robotic Assembly: From Sequence Inference to Contact Selection | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611259/ | [
"Xinghao Zhu",
"Devesh K. Jha",
"Diego Romeres",
"Lingfeng Sun",
"Masayoshi Tomizuka",
"Anoop Cherian",
"Xinghao Zhu",
"Devesh K. Jha",
"Diego Romeres",
"Lingfeng Sun",
"Masayoshi Tomizuka",
"Anoop Cherian"
] | Automating the assembly of objects from their parts is a complex problem with innumerable applications in manufacturing, maintenance, and recycling. Unlike existing research, which is limited to target segmentation, pose regression, or using fixed target blueprints, our work presents a holistic multi-level framework for part assembly planning consisting of part assembly sequence inference, part mo... |
Learning to Design 3D Printable Adaptations on Everyday Objects for Robot Manipulation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610268/ | [
"Michelle Guo",
"Ziang Liu",
"Stephen Tian",
"Zhaoming Xie",
"Jiajun Wu",
"C. Karen Liu",
"Michelle Guo",
"Ziang Liu",
"Stephen Tian",
"Zhaoming Xie",
"Jiajun Wu",
"C. Karen Liu"
] | Advancements in robot learning for object manipulation have shown promising results, yet certain everyday objects remain challenging for robots to effectively interact with. This discrepancy arises from the fact that human-designed objects are optimized for human use rather than robot manipulation. To address this gap, we propose a framework to automatically design 3D printable adaptations that ca... |
Evaluating Robustness of Visual Representations for Object Assembly Task Requiring Spatio-Geometrical Reasoning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610774/ | [
"Chahyon Ku",
"Carl Winge",
"Ryan Diaz",
"Wentao Yuan",
"Karthik Desingh",
"Chahyon Ku",
"Carl Winge",
"Ryan Diaz",
"Wentao Yuan",
"Karthik Desingh"
] | This paper primarily focuses on evaluating and benchmarking the robustness of visual representations in the context of object assembly tasks. Specifically, it investigates the alignment and insertion of objects with geometrical extrusions, commonly referred to as a peg-in-hole task. The accuracy required to detect and orient the peg and the hole geometry in SE(3) space for successful assembly pose... |
Towards Robot to Human Skill Coaching: A ML-powered IoT and HRI Platform for Martial Arts Training | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610291/ | [
"Katia Bourahmoune",
"Karlos Ishac",
"Marc Carmichael",
"Katia Bourahmoune",
"Karlos Ishac",
"Marc Carmichael"
] | Advances in human sensing and machine learning are paving the way for new applications of robotics in sports and fitness, making skill coaching smarter, easier and more accessible. Physical and social human robot interaction in particular has received special attention as a feedback mechanism for human performance augmentation. A core challenge in deploying robots that interact physically with hum... |
Towards Robo-Coach: Robot Interactive Stiffness/Position Adaptation for Human Strength and Conditioning Training | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611028/ | [
"Chenzui Li",
"Xi Wu",
"Tao Teng",
"Sylvain Calinon",
"Fei Chen",
"Chenzui Li",
"Xi Wu",
"Tao Teng",
"Sylvain Calinon",
"Fei Chen"
] | Traditional strength and conditioning training relies on the utilization of free weights, such as weighted implements, to elicit external stimuli. However, this approach poses a significant challenge when attempting to modify or adjust the loads within a single training set. This paper introduces an innovative method for achieving adjustable loads during resistance training by leveraging physical ... |
Model Predictive Control with Graph Dynamics for Garment Opening Insertion during Robot-Assisted Dressing | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611478/ | [
"Stelios Kotsovolis",
"Yiannis Demiris",
"Stelios Kotsovolis",
"Yiannis Demiris"
] | Robots have a great potential to help people with movement limitations in activities of daily living, such as dressing. A common problem in almost all dressing tasks is the insertion of a garment’s opening around a part of the human body. The rich contact environment and the deformations of the garment make the task a challenging problem for robots. In this paper, we propose a bi-manual control me... |
Comparison of Rating Scale and Pairwise Comparison Methods for Measuring Human Co-worker Subjective Impression of Robot during Physical Human-Robot Collaboration | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611050/ | [
"Qiao Wang",
"Ziqi Wang",
"Marc G. Carmichael",
"Dikai Liu",
"Chin-Teng Lin",
"Qiao Wang",
"Ziqi Wang",
"Marc G. Carmichael",
"Dikai Liu",
"Chin-Teng Lin"
] | The Rating Scale method has been long deemed the standard for measuring subjective perceptions. However, in the field of physical human-robot collaboration (pHRC), its aptness should be put under scrutiny due to inherent challenges such as response bias, between-subject variations, and the granularity nature.Individual variances can introduce significant bias in the rating scale results. A high gr... |
A transtibial prosthesis using a parallel spring mechanism | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610725/ | [
"Donggyu Jung",
"Shinsuk Park",
"Junho Choi",
"Donggyu Jung",
"Shinsuk Park",
"Junho Choi"
] | Prosthetic legs have been used to restore function in the lower limbs lost due to amputation. Early designs including prosthetic legs with a passive joint or without any joint as well as the Energy Storing and Releasing (ESR) feet have shown deficiency in push-off torque, which results in asymmetric gait pattern, slower walking speed, and higher cost of transportation. Although powered prosthetic ... |
Deep Learning based acoustic measurement approach for robotic applications on orthopedics | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611713/ | [
"Bangyu Lan",
"Momen Abayazid",
"Nico Verdonschot",
"Stefano Stramigioli",
"Kenan Niu",
"Bangyu Lan",
"Momen Abayazid",
"Nico Verdonschot",
"Stefano Stramigioli",
"Kenan Niu"
] | In Total Knee Replacement Arthroplasty (TKA), surgical robotics can provide image-guided navigation to fit implants with high precision. Its tracking approach highly relies on inserting bone pins into the bones tracked by the optical tracking system. This is normally done by invasive, radiative manners (implantable markers and CT scans), which introduce unnecessary trauma and prolong the preparati... |
Towards a Unified Approach for Continuously-Variable Impedance Control of Powered Prosthetic Legs over Walking Speeds and Inclines | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610071/ | [
"Albert J. Lee",
"Curt A. Laubscher",
"T. Kevin Best",
"Robert D. Gregg",
"Albert J. Lee",
"Curt A. Laubscher",
"T. Kevin Best",
"Robert D. Gregg"
] | Research in powered prosthesis control has explored the use of impedance-based control algorithms due to their biomimetic capabilities and intuitive structure. Modern impedance controllers feature parameters that smoothly vary over gait phase and task according to a data-driven model. However, these recent efforts only use continuous impedance control during stance and instead utilize discrete tra... |
Short term after-effects of small force fields applied by an upper-limb exoskeleton on inter-joint coordination | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610645/ | [
"Océane Dubois",
"Agnès Roby-Brami",
"Ross Parry",
"Nathanaël Jarrassé",
"Océane Dubois",
"Agnès Roby-Brami",
"Ross Parry",
"Nathanaël Jarrassé"
] | Exoskeleton technologies have numerous potential applications, ranging from improving human motor skills to aiding individuals in their daily activities. While exoskeletons are increasingly viewed, for example, as promising tools in industrial ergonomics, the effect of using them on human motor control, particularly on inter-joint coordination, remains relatively uncharted. This paper investigates... |
Real-time Dexterous Prosthesis Hand Control by Decoding Neural Information Based on EMG Decomposition | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611356/ | [
"Zhenzhi. Ying",
"Xianyu. Zhang",
"Shihao. Li",
"Koki. Nakashima",
"Liming. Shu",
"Naohiko. Sugita",
"Zhenzhi. Ying",
"Xianyu. Zhang",
"Shihao. Li",
"Koki. Nakashima",
"Liming. Shu",
"Naohiko. Sugita"
] | The vague interpretation of myoelectrical signals on the residual limb end makes restoring dexterous hand function in amputees still impossible. Understanding motor control between human motion intention and synaptic inputs to motor neurons also remains a significant challenge. The neural decoding methods of surface EMG signals remains challenging, which limit the application of robot hand in real... |
The Un-Kidnappable Robot: Acoustic Localization of Sneaking People | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611514/ | [
"Mengyu Yang",
"Patrick Grady",
"Samarth Brahmbhatt",
"Arun Balajee Vasudevan",
"Charles C. Kemp",
"James Hays",
"Mengyu Yang",
"Patrick Grady",
"Samarth Brahmbhatt",
"Arun Balajee Vasudevan",
"Charles C. Kemp",
"James Hays"
] | How easy is it to sneak up on a robot? We examine whether we can detect people using only the incidental sounds they produce as they move, even when they try to be quiet. To do so, we first collect a robotic dataset of high-quality 4-channel audio paired with 360° RGB data of people moving in different indoor settings. Using this dataset, we train models to predict if there is a moving person near... |
Predicting the Intention to Interact with a Service Robot: the Role of Gaze Cues | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610289/ | [
"Simone Arreghini",
"Gabriele Abbate",
"Alessandro Giusti",
"Antonio Paolillo",
"Simone Arreghini",
"Gabriele Abbate",
"Alessandro Giusti",
"Antonio Paolillo"
] | For a service robot, it is crucial to perceive as early as possible that an approaching person intends to interact: in this case, it can proactively enact friendly behaviors that lead to an improved user experience. We solve this perception task with a sequence-to-sequence classifier of a potential user intention to interact, which can be trained in a self-supervised way. Our main contribution is ... |
Non-Verbal Cues on Robot-Group Persuasion | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611310/ | [
"Alexandra Gonçalves",
"Plinio Moreno",
"Jodi Forlizzi",
"Leonel Garcia Marques",
"Alexandre Bernardino",
"Alexandra Gonçalves",
"Plinio Moreno",
"Jodi Forlizzi",
"Leonel Garcia Marques",
"Alexandre Bernardino"
] | When integrating robots into human daily life, persuasive power can be essential. However, there are often group dynamics which can complicate persuasion. This study focuses on how non-verbal cues, specifically gaze and hand gestures, affect the persuasiveness of a social robot. We have designed a protocol to include non-verbal cues in the social robot Vizzy (head and eye gaze, hand gestures) and ... |
Language and Sketching: An LLM-driven Interactive Multimodal Multitask Robot Navigation Framework | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10611462/ | [
"Weiqin Zu",
"Wenbin Song",
"Ruiqing Chen",
"Ze Guo",
"Fanglei Sun",
"Zheng Tian",
"Wei Pan",
"Jun Wang",
"Weiqin Zu",
"Wenbin Song",
"Ruiqing Chen",
"Ze Guo",
"Fanglei Sun",
"Zheng Tian",
"Wei Pan",
"Jun Wang"
] | The socially-aware navigation system has evolved to adeptly avoid various obstacles while performing multiple tasks, such as point-to-point navigation, human-following, and -guiding. However, a prominent gap persists: in Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), the procedure of communicating commands to robots demands intricate mathematical formulations. Furthermore, the transition between tasks does not qu... |
Dual-modal Tactile E-skin: Enabling Bidirectional Human-Robot Interaction via Integrated Tactile Perception and Feedback | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610074/ | [
"Shilong Mu",
"Runze Zhao",
"Zenan Lin",
"Yan Huang",
"Shoujie Li",
"Chenchang Li",
"Xiao-Ping Zhang",
"Wenbo Ding",
"Shilong Mu",
"Runze Zhao",
"Zenan Lin",
"Yan Huang",
"Shoujie Li",
"Chenchang Li",
"Xiao-Ping Zhang",
"Wenbo Ding"
] | To foster an immersive and natural human-robot interaction (HRI), the implementation of tactile perception and feedback becomes imperative, effectively bridging the conventional sensory gap. In this paper, we propose a dual-modal electronic skin (e-skin) that integrates magnetic tactile sensing and vibration feedback for enhanced HRI. The dual-modal tactile e-skin offers multi-functional tactile s... |
CAMInterHand: Cooperative Attention for Multi-View Interactive Hand Pose and Mesh Reconstruction | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610469/ | [
"Guwen Han",
"Qi Ye",
"Anjun Chen",
"Jiming Chen",
"Guwen Han",
"Qi Ye",
"Anjun Chen",
"Jiming Chen"
] | Interactive hand mesh reconstruction from singleview images poses a significant challenge with the severe occlusion and depth ambiguity inherent in interactive hand gestures. Recent approaches that employ probabilistic models and tokenpruned techniques have shown decent results in multi-view human body reconstruction. Nevertheless, these methods have not fully utilized multi-scale semantic informa... |
ICRA 2024 Accepted Paper Meta Info Dataset
This dataset is collect from the ICRA 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2024 accepted papers' meta info (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/conhome/10609961/proceeding) as well as the arxiv website DeepNLP paper arxiv (http://www.deepnlp.org/content/paper/icra2024). For researchers who are interested in doing analysis of ICRA 2024 accepted papers and potential trends, you can use the already cleaned up json files. Each row contains the meta information of a paper in the ICRA 2024 conference. To explore more AI & Robotic papers (NIPS/ICML/ICLR/IROS/ICRA/etc) and AI equations, feel free to navigate the Equation Search Engine (http://www.deepnlp.org/search/equation) as well as the AI Agent Search Engine to find the deployed AI Apps and Agents (http://www.deepnlp.org/search/agent) in your domain.
Equations Latex code and Papers Search Engine
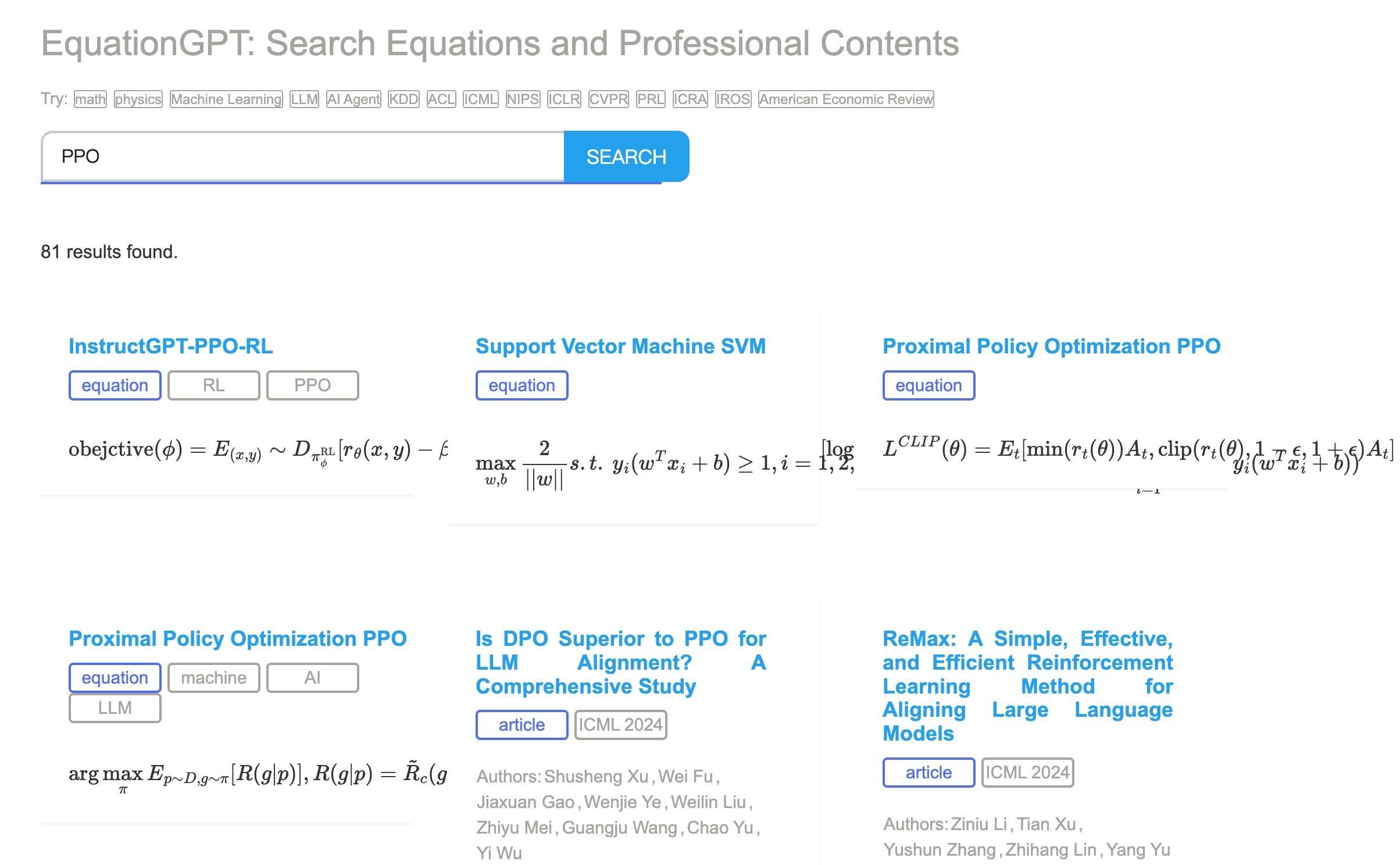
Meta Information of Json File of Paper
{
"title": "TinyMPC: Model-Predictive Control on Resource-Constrained Microcontrollers",
"detail_url": "https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10610987/",
"author_list": ["Khai Nguyen", "Sam Schoedel", "Anoushka Alavilli", "Brian Plancher", "Zachary Manchester", "Khai Nguyen", "Sam Schoedel", "Anoushka Alavilli", "Brian Plancher", "Zachary Manchester"],
"abstract": "Model-predictive control (MPC) is a powerful tool for controlling highly dynamic robotic systems subject to complex constraints. However, MPC is computationally demanding, and is often impractical to implement on small, resource-constrained robotic platforms. We present TinyMPC, a high-speed MPC solver with a low memory footprint targeting the microcontrollers common on small robots. Our approach ..."
}
Related
AI Agent Marketplace and Search
AI Agent Marketplace and Search
Robot Search
Equation and Academic search
AI & Robot Comprehensive Search
AI & Robot Question
AI & Robot Community
AI Agent Marketplace Blog
AI Agent Reviews
AI Agent Marketplace Directory
Microsoft AI Agents Reviews
Claude AI Agents Reviews
OpenAI AI Agents Reviews
Saleforce AI Agents Reviews
AI Agent Builder Reviews
AI Equation
List of AI Equations and Latex
List of Math Equations and Latex
List of Physics Equations and Latex
List of Statistics Equations and Latex
List of Machine Learning Equations and Latex
- Downloads last month
- 28