title
stringlengths 7
164
| detail_url
stringlengths 27
45
| author_list
sequencelengths 0
40
| abstract
stringlengths 0
403
|
|---|---|---|---|
[IROS 2021 Front cover] | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | [IROS 2021 Front cover] |
[IROS 2021 Title page] | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | [IROS 2021 Title page] |
Preface | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635971/ | [] | |
Organizing Committee | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636726/ | [] | |
Technical Program at Glance | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | Technical Program at Glance |
Plenaries and keynotes | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636699/ | [] | Provides an abstract for each of the invited presentations and may include a brief professional biography of each presenter. The complete presentations were not made available for publication as part of the conference proceedings. |
Index of Papers | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | |
Index of Papers | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org | [] | |
Up-to-Down Network: Fusing Multi-Scale Context for 3D Semantic Scene Completion | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635888/ | [
"Hao Zou",
"Xuemeng Yang",
"Tianxin Huang",
"Chujuan Zhang",
"Yong Liu",
"Wanlong Li",
"Feng Wen",
"Hongbo Zhang",
"Hao Zou",
"Xuemeng Yang",
"Tianxin Huang",
"Chujuan Zhang",
"Yong Liu",
"Wanlong Li",
"Feng Wen",
"Hongbo Zhang"
] | An efficient 3D scene perception algorithm is a vital component for autonomous driving and robotics systems. In this paper, we focus on semantic scene completion, which is a task of jointly estimating the volumetric occupancy and semantic labels of objects. Since the real-world data is sparse and occluded, this is an extremely challenging task. We propose a novel framework, named Up-to-Down networ... |
Memory-based Semantic Segmentation for Off-road Unstructured Natural Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636620/ | [
"Youngsaeng Jin",
"David Han",
"Hanseok Ko",
"Youngsaeng Jin",
"David Han",
"Hanseok Ko"
] | With the availability of many datasets tailored for autonomous driving in real-world urban scenes, semantic segmentation for urban driving scenes achieves significant progress. However, semantic segmentation for off-road, unstructured environments is not widely studied. Directly applying existing segmentation networks often results in performance degradation as they cannot overcome intrinsic probl... |
A Deep Learning-based Indoor Scene Classification Approach Enhanced with Inter-Object Distance Semantic Features | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636242/ | [
"Ricardo Pereira",
"Luís Garrote",
"Tiago Barros",
"Ana Lopes",
"Urbano J. Nunes",
"Ricardo Pereira",
"Luís Garrote",
"Tiago Barros",
"Ana Lopes",
"Urbano J. Nunes"
] | Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have been increasingly applied in visual classification tasks by replacing hand-crafted features with deep features. However, problems such as inter-class similarity and intra-class variation led to the need of obtaining more descriptive features. To accomplish this, a new semantic inter-object relationship approach is proposed, which is based on the distance r... |
BORM: Bayesian Object Relation Model for Indoor Scene Recognition | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636024/ | [
"Liguang Zhou",
"Jun Cen",
"Xingchao Wang",
"Zhenglong Sun",
"Tin Lun Lam",
"Yangsheng Xu",
"Liguang Zhou",
"Jun Cen",
"Xingchao Wang",
"Zhenglong Sun",
"Tin Lun Lam",
"Yangsheng Xu"
] | Scene recognition is a fundamental task in robotic perception. For human beings, scene recognition is reasonable because they have abundant object knowledge of the real world. The idea of transferring prior object knowledge from humans to scene recognition is significant but still less exploited. In this paper, we propose to utilize meaningful object representations for indoor scene representation... |
CORSAIR: Convolutional Object Retrieval and Symmetry-AIded Registration | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636347/ | [
"Tianyu Zhao",
"Qiaojun Feng",
"Sai Jadhav",
"Nikolay Atanasov",
"Tianyu Zhao",
"Qiaojun Feng",
"Sai Jadhav",
"Nikolay Atanasov"
] | This paper considers online object-level mapping using partial point-cloud observations obtained online in an unknown environment. We develop an approach for fully Convolutional Object Retrieval and Symmetry-AIded Registration (CORSAIR). Our model extends the Fully Convolutional Geo-metric Features model to learn a global object-shape embedding in addition to local point-wise features from the poi... |
Real-Time Monocular Human Depth Estimation and Segmentation on Embedded Systems | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636518/ | [
"Shan An",
"Fangru Zhou",
"Mei Yang",
"Haogang Zhu",
"Changhong Fu",
"Konstantinos A. Tsintotas",
"Shan An",
"Fangru Zhou",
"Mei Yang",
"Haogang Zhu",
"Changhong Fu",
"Konstantinos A. Tsintotas"
] | Estimating a scene’s depth to achieve collision avoidance against moving pedestrians is a crucial and fundamental problem in the robotic field. This paper proposes a novel, low complexity network architecture for fast and accurate human depth estimation and segmentation in indoor environments, aiming to applications for resource-constrained platforms (including battery-powered aerial, micro-aerial... |
Joint Depth and Normal Estimation from Real-world Time-of-flight Raw Data | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636508/ | [
"Rongrong Gao",
"Na Fan",
"Changlin Li",
"Wentao Liu",
"Qifeng Chen",
"Rongrong Gao",
"Na Fan",
"Changlin Li",
"Wentao Liu",
"Qifeng Chen"
] | We present a novel approach to joint depth and normal estimation for time-of-flight (ToF) sensors. Our model learns to predict the high-quality depth and normal maps jointly from ToF raw sensor data. To achieve this, we meticulously constructed the first large-scale dataset (named ToF-100) with paired raw ToF data and ground-truth high-resolution depth maps provided by an industrial depth camera. ... |
On the descriptive power of LiDAR intensity images for segment-based loop closing in 3-D SLAM | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636698/ | [
"Jan Wietrzykowski",
"Piotr Skrzypczyński",
"Jan Wietrzykowski",
"Piotr Skrzypczyński"
] | We propose an extension to the segment-based global localization method for LiDAR SLAM using descriptors learned considering the visual context of the segments. A new architecture of the deep neural network is presented that learns the visual context acquired from synthetic LiDAR intensity images. This approach allows a single multi-beam LiDAR to produce rich and highly descriptive location signat... |
Learning State-Dependent Sensor Measurement Models with Limited Sensor Measurements | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636407/ | [
"Troi Williams",
"Yu Sun",
"Troi Williams",
"Yu Sun"
] | We present a two-stage transfer learning method for training state-dependent sensor measurement models (SDSMMs) with limited sensor data. This method can alleviate collecting sizeable sensor and ground truth data to learn accurate sensor models, especially when we must learn many sensor models (for example, a fleet of autonomous cars, drones, or warehouse robots). In the first stage, we use prior ... |
Self-calibrated dense 3D sensor using multiple cross line-lasers based on light sectioning method and visual odometry | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636505/ | [
"Genki Nagamatsu",
"Jun Takamatsu",
"Takafumi Iwaguchi",
"Diego Thomas",
"Hiroshi Kawasaki",
"Genki Nagamatsu",
"Jun Takamatsu",
"Takafumi Iwaguchi",
"Diego Thomas",
"Hiroshi Kawasaki"
] | Among various 3D capturing systems, since the system with line lasers based on the light sectioning method is simple and accurate, it has widely attracted many developers and used for many purposes. In addition, there is no need to synchronize the camera and the laser and also the configuration of the camera and the lasers is flexible, and thus, the system can be used for extreme conditions, such ... |
Obstacle Avoidance onboard MAVs using a FMCW Radar | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635901/ | [
"Nikhil Wessendorp",
"Raoul Dinaux",
"Julien Dupeyroux",
"Guido C. H. E. de Croon",
"Nikhil Wessendorp",
"Raoul Dinaux",
"Julien Dupeyroux",
"Guido C. H. E. de Croon"
] | Micro Air Vehicles (MAVs) are increasingly being used for complex or hazardous tasks in enclosed and cluttered environments such as surveillance or search and rescue. With this comes the necessity for sensors that can operate in poor visibility conditions to facilitate with navigation and avoidance of objects or people. Radar sensors in particular can provide more robust sensing of the environment... |
Gaussian Process-based Interpretable Runtime Adaptation for Safe Autonomous Systems Operations in Unstructured Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636490/ | [
"Christian Gall",
"Nicola Bezzo",
"Christian Gall",
"Nicola Bezzo"
] | Autonomous vehicles may not behave as expected when subject to environmental disturbances. For instance, control commands suitable for driving on dry, paved roads may lead to unsafe conditions and undesired deviations when on slippery dirt or icy roads. Furthermore, it becomes increasingly important to offer human-understandable explanations of autonomous robots’ actions – especially when they ope... |
Latent Attention Augmentation for Robust Autonomous Driving Policies | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636449/ | [
"Ran Cheng",
"Christopher Agia",
"Florian Shkurti",
"David Meger",
"Gregory Dudek",
"Ran Cheng",
"Christopher Agia",
"Florian Shkurti",
"David Meger",
"Gregory Dudek"
] | Model-free reinforcement learning has become a viable approach for vision-based robot control. However, sample complexity and adaptability to domain shifts remain persistent challenges when operating in high-dimensional observation spaces (images, LiDAR), such as those that are involved in autonomous driving. In this paper, we propose a flexible framework by which a policy’s observations are augme... |
From Agile Ground to Aerial Navigation: Learning from Learned Hallucination | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636402/ | [
"Zizhao Wang",
"Xuesu Xiao",
"Alexander J Nettekoven",
"Kadhiravan Umasankar",
"Anika Singh",
"Sriram Bommakanti",
"Ufuk Topcu",
"Peter Stone",
"Zizhao Wang",
"Xuesu Xiao",
"Alexander J Nettekoven",
"Kadhiravan Umasankar",
"Anika Singh",
"Sriram Bommakanti",
"Ufuk Topcu",
"Peter Stone"
] | This paper presents a self-supervised Learning from Learned Hallucination (LfLH) method to learn fast and reactive motion planners for ground and aerial robots to navigate through highly constrained environments. The recent Learning from Hallucination (LfH) paradigm for autonomous navigation executes motion plans by random exploration in completely safe obstacle-free spaces, uses hand-crafted hall... |
Robust Policy Search for an Agile Ground Vehicle Under Perception Uncertainty | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636552/ | [
"Shahriar Sefati",
"Subhransu Mishra",
"Matthew Sheckells",
"Kapil D. Katyal",
"Jin Bai",
"Gregory D. Hager",
"Marin Kobilarov",
"Shahriar Sefati",
"Subhransu Mishra",
"Matthew Sheckells",
"Kapil D. Katyal",
"Jin Bai",
"Gregory D. Hager",
"Marin Kobilarov"
] | Learning robust policies for robotic systems operating in presence of uncertainty is a challenging task. For safe navigation, in addition to the natural stochasticity of the environment and vehicle dynamics, the perception uncertainty associated with dynamic entities, e.g. pedestrians, must be accounted for during motion planning. To this end, we construct an algorithm with built-in robustness to ... |
Road Graphical Neural Networks for Autonomous Roundabout Driving | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636411/ | [
"Timothy Ha",
"Gunmin Lee",
"Dohyeong Kim",
"Songhwai Oh",
"Timothy Ha",
"Gunmin Lee",
"Dohyeong Kim",
"Songhwai Oh"
] | We propose a novel autonomous driving frame-work that leverages graph-based features of roads, such as road positions and connections. The proposed method is divided into two parts: a low-level controller which follows the trajectory calculated by a graph-based path planner, and a high-level controller which determines the speed of the vehicle to follow the traffic flow. The high-level controller ... |
Monitoring and Diagnosability of Perception Systems | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636497/ | [
"Pasquale Antonante",
"David I. Spivak",
"Luca Carlone",
"Pasquale Antonante",
"David I. Spivak",
"Luca Carlone"
] | Perception is a critical component of high-integrity applications of robotics and autonomous systems, such as self-driving vehicles. In these applications, failure of perception systems may put human life at risk, and a broad adoption of these technologies requires the development of methodologies to guarantee and monitor safe operation. Despite the paramount importance of perception systems, curr... |
COCOI: Contact-aware Online Context Inference for Generalizable Non-planar Pushing | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636836/ | [
"Zhuo Xu",
"Wenhao Yu",
"Alexander Herzog",
"Wenlong Lu",
"Chuyuan Fu",
"Masayoshi Tomizuka",
"Yunfei Bai",
"C. Karen Liu",
"Daniel Ho",
"Zhuo Xu",
"Wenhao Yu",
"Alexander Herzog",
"Wenlong Lu",
"Chuyuan Fu",
"Masayoshi Tomizuka",
"Yunfei Bai",
"C. Karen Liu",
"Daniel Ho"
] | General contact-rich manipulation problems are long-standing challenges in robotics due to the difficulty of understanding complicated contact physics. Deep reinforcement learning (RL) has shown great potential in solving robot manipulation tasks. However, existing RL policies have limited adaptability to environments with diverse dynamics properties, which is pivotal in solving many contact-rich ... |
DeepKoCo: Efficient latent planning with a task-relevant Koopman representation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636408/ | [
"Bas van der Heijden",
"Laura Ferranti",
"Jens Kober",
"Robert Babuška",
"Bas van der Heijden",
"Laura Ferranti",
"Jens Kober",
"Robert Babuška"
] | This paper presents DeepKoCo, a novel modelbased agent that learns a latent Koopman representation from images. This representation allows DeepKoCo to plan efficiently using linear control methods, such as linear model predictive control. Compared to traditional agents, DeepKoCo learns taskrelevant dynamics, thanks to the use of a tailored lossy autoencoder network that allows DeepKoCo to learn la... |
Low Dimensional State Representation Learning with Robotics Priors in Continuous Action Spaces | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635936/ | [
"Nicolò Botteghi",
"Khaled Alaa",
"Mannes Poel",
"Beril Sirmacek",
"Christoph Brune",
"Abeje Mersha",
"Stefano Stramigioli",
"Nicolò Botteghi",
"Khaled Alaa",
"Mannes Poel",
"Beril Sirmacek",
"Christoph Brune",
"Abeje Mersha",
"Stefano Stramigioli"
] | Reinforcement learning algorithms have proven to be capable of solving complicated robotics tasks in an end-to-end fashion without any need for hand-crafted features or policies. Especially in the context of robotics, in which the cost of real-world data is usually extremely high, Reinforcement Learning solutions achieving high sample efficiency are needed. In this paper, we propose a framework co... |
Acceleration of Actor-Critic Deep Reinforcement Learning for Visual Grasping by State Representation Learning Based on a Preprocessed Input Image | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635931/ | [
"Taewon Kim",
"Yeseong Park",
"Youngbin Park",
"Sang Hyoung Lee",
"Il Hong Suh",
"Taewon Kim",
"Yeseong Park",
"Youngbin Park",
"Sang Hyoung Lee",
"Il Hong Suh"
] | For robotic grasping tasks with diverse target objects, some deep learning-based methods have achieved state-of-the-art results using direct visual input. In contrast, actor-critic deep reinforcement learning (RL) methods typically perform very poorly when applied to grasp diverse objects, especially when learning from raw images and sparse rewards. To render these RL techniques feasible for visio... |
SSTN: Self-Supervised Domain Adaptation Thermal Object Detection for Autonomous Driving | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636353/ | [
"Farzeen Munir",
"Shoaib Azam",
"Moongu Jeon",
"Farzeen Munir",
"Shoaib Azam",
"Moongu Jeon"
] | The perception of the environment plays a decisive role in the safe and secure operation of autonomous vehicles. The perception of the surrounding is way similar to human vision. The human’s brain perceives the environment by utilizing different sensory channels and develop a view-invariant representation model. In this context, different exteroceptive sensors like cameras, Lidar, are deployed on ... |
Self-Supervised Disentangled Representation Learning for Third-Person Imitation Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636363/ | [
"Jinghuan Shang",
"Michael S. Ryoo",
"Jinghuan Shang",
"Michael S. Ryoo"
] | Humans learn to imitate by observing others. However, robot imitation learning generally requires expert demonstrations in the first-person view (FPV). Collecting such FPV videos for every robot could be very expensive.Third-person imitation learning (TPIL) is the concept of learning action policies by observing other agents in a third-person view (TPV), similar to what humans do. This ultimately ... |
Learning to Drop Points for LiDAR Scan Synthesis | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636747/ | [
"Kazuto Nakashima",
"Ryo Kurazume",
"Kazuto Nakashima",
"Ryo Kurazume"
] | 3D laser scanning by LiDAR sensors plays an important role for mobile robots to understand their surroundings. Nevertheless, not all systems have high resolution and accuracy due to hardware limitations, weather conditions, and so on. Generative modeling of LiDAR data as scene priors is one of the promising solutions to compensate for unreliable or incomplete observations. In this paper, we propos... |
Unsupervised Learning of Depth Estimation and Visual Odometry for Sparse Light Field Cameras | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636570/ | [
"S. Tejaswi Digumarti",
"Joseph Daniel",
"Ahalya Ravendran",
"Ryan Griffiths",
"Donald G. Dansereau",
"S. Tejaswi Digumarti",
"Joseph Daniel",
"Ahalya Ravendran",
"Ryan Griffiths",
"Donald G. Dansereau"
] | While an exciting diversity of new imaging devices is emerging that could dramatically improve robotic perception, the challenges of calibrating and interpreting these cameras have limited their uptake in the robotics community. In this work we generalise techniques from unsupervised learning to allow a robot to autonomously interpret new kinds of cameras. We consider emerging sparse light field (... |
Lvio-Fusion: A Self-adaptive Multi-sensor Fusion SLAM Framework Using Actor-critic Method | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635905/ | [
"Yupeng Jia",
"Haiyong Luo",
"Fang Zhao",
"Guanlin Jiang",
"Yuhang Li",
"Jiaquan Yan",
"Zhuqing Jiang",
"Zitian Wang",
"Yupeng Jia",
"Haiyong Luo",
"Fang Zhao",
"Guanlin Jiang",
"Yuhang Li",
"Jiaquan Yan",
"Zhuqing Jiang",
"Zitian Wang"
] | State estimation with sensors is essential for mobile robots. Due to different performance of sensors in different environments, how to fuse measurements of various sensors is a problem. In this paper, we propose a tightly coupled multi-sensor fusion framework, Lvio-Fusion, which fuses stereo camera, Lidar, IMU, and GPS based on the graph optimization. Especially for urban traffic scenes, we intro... |
Reactive Visual Odometry Scheduling Based on Noise Analysis using an Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636214/ | [
"Mateusz Tomasz Malinowski",
"Arthur Richards",
"Mark Woods",
"Mateusz Tomasz Malinowski",
"Arthur Richards",
"Mark Woods"
] | A new strategy is proposed for scheduling Visual Odometry (VO) measurements for wheeled ground vehicles. Rather than having a fixed interval or distance between image acquisitions, we propose to trigger VO based on covariances from an Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter. The adopted model uses process noise to drive wheel slip estimation, which, when correctly identified, can be used with Wheel Odomet... |
Multi-sensor Fusion Incorporating Adaptive Transformation for Reconfigurable Pavement Sweeping Robot | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636464/ | [
"A.P. Povendhan",
"Lim Yi",
"A. A. Hayat",
"Anh Vu Le",
"K. L. J. Kai",
"B. Ramalingam",
"M. R. Elara",
"A.P. Povendhan",
"Lim Yi",
"A. A. Hayat",
"Anh Vu Le",
"K. L. J. Kai",
"B. Ramalingam",
"M. R. Elara"
] | An efficient sensors fusion framework in an autonomous robot is necessary for various functions like object detection and perception enhancement. Multi-sensor calibration techniques are used to fuse multiple static sensors into a single frame of reference. However, for reconfigurable robots, sensors can change pose during reconfiguration need a robust adaptive sensor fusion to account for the rela... |
Continuous-time Radar-inertial Odometry for Automotive Radars | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636014/ | [
"Yin Zhi Ng",
"Benjamin Choi",
"Robby Tan",
"Lionel Heng",
"Yin Zhi Ng",
"Benjamin Choi",
"Robby Tan",
"Lionel Heng"
] | We present an approach for radar-inertial odometry which uses a continuous-time framework to fuse measurements from multiple automotive radars and an inertial measurement unit (IMU). Adverse weather conditions do not have a significant impact on the operating performance of radar sensors unlike that of camera and LiDAR sensors. Radar’s robustness in such conditions and the increasing prevalence of... |
Radar Visual Inertial Odometry and Radar Thermal Inertial Odometry: Robust Navigation even in Challenging Visual Conditions | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636799/ | [
"Christopher Doer",
"Gert F. Trommer",
"Christopher Doer",
"Gert F. Trommer"
] | In this paper, we propose to fuse radar measurements with Visual Inertial Odometry (RVIO) or Thermal Inertial Odometry (RTIO). FMCW radar sensor data enables to estimate the 3D ego velocity independent of the visual conditions. Fusion with VIO or TIO heavily improves the robustness in challenging conditions such as darkness, direct sunlight or fog.Specifically, we propose RRxIO: An extension to th... |
B-spline path planner for safe navigation of mobile robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636612/ | [
"Ngoc Thinh Nguyen",
"Lars Schilling",
"Michael Sebastian Angern",
"Heiko Hamann",
"Floris Ernst",
"Georg Schildbach",
"Ngoc Thinh Nguyen",
"Lars Schilling",
"Michael Sebastian Angern",
"Heiko Hamann",
"Floris Ernst",
"Georg Schildbach"
] | We propose a 2D path planning algorithm in a non-convex workspace defined as a sequence of connected convex polytopes. The reference path is parameterized as a B-spline curve, which is guaranteed to entirely remain within the workspace by exploiting the local convexity property and by formulating linear constraints on the control points of the B-spline. The novelties of the paper lie in the use of... |
Closed-loop Fast Marching Tree (CL-FMT*) with Application to Helicopter Landing Trajectory Planning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636509/ | [
"Navid Dadkhah Tehrani",
"Igor Cherepinsky",
"Sean Carlson",
"Navid Dadkhah Tehrani",
"Igor Cherepinsky",
"Sean Carlson"
] | Motion planning for complex dynamic systems such as helicopters is a challenging problem due to non-holonomic and nonlinear differential constraints. Approaches for optimal kinodynamics motion planning have only been demonstrated for simple dynamic systems such as Dubins car or linear systems. In this paper we present Closed-loop FMT* (CL-FMT*) which is an extension of FMT* [7] that uses closed-lo... |
Exploring Learning for Intercepting Projectiles with a Robot-Held Stick | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635993/ | [
"John E. G. Baxter",
"Torin Adamson",
"Satomi Sugaya",
"Lydia Tapia",
"John E. G. Baxter",
"Torin Adamson",
"Satomi Sugaya",
"Lydia Tapia"
] | For many tasks, including table tennis, catching, and sword fighting, a critical step is intercepting the incoming object with a robot arm or held tool. Solutions to robot arm interception via learning, specifically reinforcement learning (RL), have become prevalent, as they provide robust solutions to the robot arm interception problem, even for high degree of freedom robotic systems. Despite num... |
Disruption-Limited Planning for Robot Navigation in Dynamic Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636274/ | [
"Sandip Aine",
"Yash Oza",
"Maxim Likhachev",
"Sandip Aine",
"Yash Oza",
"Maxim Likhachev"
] | Path planning in the presence of dynamic obstacles is a fundamental problem in robotics with widespread applications. A typical approach to such problems is that a robot predicts the trajectories of dynamic obstacles, and plans its path while avoiding them. Such a formulation becomes limiting though for scenarios where an agent cannot complete its task efficiently, without disrupting the movement ... |
Spatial Constraint Generation for Motion Planning in Dynamic Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636067/ | [
"Han Hu",
"Peyman Yadmellat",
"Han Hu",
"Peyman Yadmellat"
] | This paper presents a novel method to generate spatial constraints for motion planning in dynamic environments. Motion planning methods for autonomous driving and mobile robots typically need to rely on the spatial constraints imposed by a map-based global planner to generate a collision-free trajectory. These methods may fail without an offline map or where the map is invalid due to dynamic chang... |
Optimal scheduling and non-cooperative distributed model predictive control for multiple robotic manipulators | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636118/ | [
"Nigora Gafur",
"Vassilios Yfantis",
"Martin Ruskowski",
"Nigora Gafur",
"Vassilios Yfantis",
"Martin Ruskowski"
] | Application of multiple robotic manipulators in a shared workspace is still restricted to repetitive tasks limiting their flexible deployment for production systems. Still, existing motion control algorithms cannot be performed online for arbitrary environments in case of multiple manipulators cooperating with each other. In this work we propose a scalable and real-time capable motion control algo... |
OneVision: Centralized to Distributed Controller Synthesis with Delay Compensation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636164/ | [
"Jiayi Wei",
"Tongrui Li",
"Swarat Chaudhuri",
"Isil Dillig",
"Joydeep Biswas",
"Jiayi Wei",
"Tongrui Li",
"Swarat Chaudhuri",
"Isil Dillig",
"Joydeep Biswas"
] | We propose a new algorithm to simplify the controller development for distributed robotic systems subject to external observations, disturbances, and communication delays. Unlike prior approaches that propose specialized solutions to handling communication latency for specific robotic applications, our algorithm uses an arbitrary centralized controller as the specification and automatically genera... |
Robofleet: Open Source Communication and Management for Fleets of Autonomous Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635830/ | [
"Kavan Singh Sikand",
"Logan Zartman",
"Sadegh Rabiee",
"Joydeep Biswas",
"Kavan Singh Sikand",
"Logan Zartman",
"Sadegh Rabiee",
"Joydeep Biswas"
] | Long-term deployment of a fleet of mobile robots requires reliable and secure two-way communication channels between individual robots and remote human operators for supervision and tasking. Existing open-source solutions to this problem degrade in performance in challenging real-world situations such as intermittent and low-bandwidth connectivity, do not provide security control options, and can ... |
Learning Connectivity for Data Distribution in Robot Teams | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636873/ | [
"Ekaterina Tolstaya",
"Landon Butler",
"Daniel Mox",
"James Paulos",
"Vijay Kumar",
"Alejandro Ribeiro",
"Ekaterina Tolstaya",
"Landon Butler",
"Daniel Mox",
"James Paulos",
"Vijay Kumar",
"Alejandro Ribeiro"
] | Many algorithms for control of multi-robot teams operate under the assumption that low-latency, global state information necessary to coordinate agent actions can readily be disseminated among the team. However, in harsh environments with no existing communication infrastructure, robots must form ad-hoc networks, forcing the team to operate in a distributed fashion. To overcome this challenge, we ... |
Deadlock Prediction and Recovery for Distributed Collision Avoidance with Buffered Voronoi Cells | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636609/ | [
"Mohammed Abdullhak",
"Andrew Vardy",
"Mohammed Abdullhak",
"Andrew Vardy"
] | This paper introduces a distributed multi-robot collision avoidance algorithm based on the concept of Buffered Voronoi Cells (BVC). We propose a novel algorithm for avoiding deadlocks consisting of three stages: deadlock prediction, deadlock recovery, and deadlock recovery success prediction. Simple heuristics (such as the right-hand rule) are often used to avoid deadlocks. Such heuristics might r... |
Scalable Distributed Planning for Multi-Robot, Multi-Target Tracking | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636729/ | [
"Micah Corah",
"Nathan Michael",
"Micah Corah",
"Nathan Michael"
] | In multi-robot multi-target tracking, robots coordinate to monitor groups of targets moving about an environment. We approach planning for such scenarios by formulating a receding-horizon, multi-robot sensing problem with a mutual information objective. Such problems are NP-Hard in general. Yet, our objective is submodular which enables certain greedy planners to guarantee constant-factor suboptim... |
Motion Field Consensus with Locality Preservation: A Geometric Confirmation Strategy for Loop Closure Detection | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636769/ | [
"Kaining Zhang",
"Xingyu Jiang",
"Xiaoguang Mei",
"Huabing Zhou",
"Jiayi Ma",
"Kaining Zhang",
"Xingyu Jiang",
"Xiaoguang Mei",
"Huabing Zhou",
"Jiayi Ma"
] | Loop closure detection (LCD), which aims to deal with the drift emerging when robots travel around the route, plays a key role in a simultaneous localization and mapping system. Unlike most current methods which focus on seeking an appropriate representation of images, we propose a novel two-stage pipeline dominated by the estimation of spatial geometric relationship. When a query image occurs, we... |
Re-Attention Is All You Need: Memory-Efficient Scene Text Detection via Re-Attention on Uncertain Regions | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636510/ | [
"Hsiang-Chun Chang",
"Hung-Jen Chen",
"Yu-Chia Shen",
"Hong-Han Shuai",
"Wen-Huang Cheng",
"Hsiang-Chun Chang",
"Hung-Jen Chen",
"Yu-Chia Shen",
"Hong-Han Shuai",
"Wen-Huang Cheng"
] | Scene text detection plays an important role on vision-based robot navigation to many potential landmarks such as nameplates, information signs, floor button in the elevators. Recently, scene text detection with segmentation-based methods has been receiving more and more attention. The segmentation results can be used to efficiently predict scene text of various shapes, such as irregular text in m... |
Trajectory-Constrained Deep Latent Visual Attention for Improved Local Planning in Presence of Heterogeneous Terrain | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636422/ | [
"Stefan Wapnick",
"Travis Manderson",
"David Meger",
"Gregory Dudek",
"Stefan Wapnick",
"Travis Manderson",
"David Meger",
"Gregory Dudek"
] | We present a reward-predictive, model-based learning method featuring trajectory-constrained visual attention for use in mapless, local visual navigation tasks. Our method learns to place visual attention at locations in latent image space which follow trajectories caused by vehicle control actions to later enhance predictive accuracy during planning. Our attention model is jointly optimized by th... |
Learning Navigation Skills for Legged Robots with Learned Robot Embeddings | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635911/ | [
"Joanne Truong",
"Denis Yarats",
"Tianyu Li",
"Franziska Meier",
"Sonia Chernova",
"Dhruv Batra",
"Akshara Rai",
"Joanne Truong",
"Denis Yarats",
"Tianyu Li",
"Franziska Meier",
"Sonia Chernova",
"Dhruv Batra",
"Akshara Rai"
] | Recent work has shown results on learning navigation policies for idealized cylinder agents in simulation and transferring them to real wheeled robots. Deploying such navigation policies on legged robots can be challenging due to their complex dynamics, and the large dynamical difference between cylinder agents and legged systems. In this work, we learn hierarchical navigation policies that accoun... |
NavTuner: Learning a Scene-Sensitive Family of Navigation Policies | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636185/ | [
"Haoxin Ma",
"Justin S. Smith",
"Patricio A. Vela",
"Haoxin Ma",
"Justin S. Smith",
"Patricio A. Vela"
] | The advent of deep learning has inspired research into end-to-end learning for a variety of problem domains in robotics. For navigation, the resulting methods may not have the generalization properties desired let alone match the performance of traditional methods. Instead of learning a navigation policy, we explore learning an adaptive policy in the parameter space of an existing navigation modul... |
Fast and Robust Bio-inspired Teach and Repeat Navigation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636334/ | [
"Dominic Dall’Osto",
"Tobias Fischer",
"Michael Milford",
"Dominic Dall’Osto",
"Tobias Fischer",
"Michael Milford"
] | Fully autonomous mobile robots have a multitude of potential applications, but guaranteeing robust navigation performance remains an open research problem. For many tasks such as repeated infrastructure inspection, item delivery, or inventory transport, a route repeating capability can be sufficient and offers potential practical advantages over a full navigation stack. Previous teach and repeat r... |
Using Depth Vision for Terrain Detection during Active Locomotion | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636077/ | [
"Ali H. A. Al-dabbagh",
"Renaud Ronsse",
"Ali H. A. Al-dabbagh",
"Renaud Ronsse"
] | Vision-based systems for terrain detection are ubiquitous in mobile robotics, while such systems recently emerged for locomotion assistance of disabled people. For instance, wearable devices embedding vision sensors can assist people in navigation; or guide lower-limb prosthesis or exoskeleton controller to retrieve gait patterns being adapted to the executed task (overground walking, stairs, slop... |
Robust and Accurate Point Set Registration with Generalized Bayesian Coherent Point Drift | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635908/ | [
"Ang Zhang",
"Zhe Min",
"Jin Pan",
"Max Q.-H. Meng",
"Ang Zhang",
"Zhe Min",
"Jin Pan",
"Max Q.-H. Meng"
] | Point set registration (PSR) is an essential problem in surgical navigation and image-guided surgery (IGS). It can help align the pre-operative volumetric images with the intra-operative surgical space. The performances of PSR are susceptible to noise and outliers, which are the cases in real-world surgical scenarios. In this paper, we provide a novel point set registration method that utilizes th... |
Localization and Control of Magnetic Suture Needles in Cluttered Surgical Site with Blood and Tissue | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636441/ | [
"Will Pryor",
"Yotam Barnoy",
"Suraj Raval",
"Xiaolong Liu",
"Lamar Mair",
"Daniel Lerner",
"Onder Erin",
"Gregory D. Hager",
"Yancy Diaz-Mercado",
"Axel Krieger",
"Will Pryor",
"Yotam Barnoy",
"Suraj Raval",
"Xiaolong Liu",
"Lamar Mair",
"Daniel Lerner",
"Onder Erin",
"Gregory D. Hager",
"Yancy Diaz-Mercado",
"Axel Krieger"
] | Real-time visual localization of needles is necessary for various surgical applications, including surgical automation and visual feedback. In this study we investigate localization and autonomous robotic control of needles in the context of our magneto-suturing system. Our system holds the potential for surgical manipulation with the benefit of minimal invasiveness and reduced patient side effect... |
LaneRCNN: Distributed Representations for Graph-Centric Motion Forecasting | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636035/ | [
"Wenyuan Zeng",
"Ming Liang",
"Renjie Liao",
"Raquel Urtasun",
"Wenyuan Zeng",
"Ming Liang",
"Renjie Liao",
"Raquel Urtasun"
] | Forecasting the future behaviors of dynamic actors is an important task in many robotics applications such as self-driving. It is extremely challenging as actors have latent intentions and their trajectories are governed by complex interactions between the other actors, themselves, and the map. In this paper, we propose LaneRCNN, a graph-centric motion forecasting model that captures the actor-to-... |
StereoCNC: A Stereovision-guided Robotic Laser System | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636050/ | [
"Guangshen Ma",
"Weston Ross",
"Patrick J. Codd",
"Guangshen Ma",
"Weston Ross",
"Patrick J. Codd"
] | This paper proposes a stereovision-guided robotic laser system that can conduct laser ablation on targets selected by human operators in the color image, referred as StereoCNC. Two digital cameras are integrated into a previously developed robotic laser system to add a color sensing modality and formulate the stereovision. A calibration method is implemented to register the coordinate frames betwe... |
Direct Bundle Adjustment for 3D Image Fusion with Application to Transesophageal Echocardiography | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636721/ | [
"Zhehua Mao",
"Liang Zhao",
"Shoudong Huang",
"Yiting Fan",
"Alex Pui-Wai Lee",
"Zhehua Mao",
"Liang Zhao",
"Shoudong Huang",
"Yiting Fan",
"Alex Pui-Wai Lee"
] | In this paper, we propose a novel algorithm for fusing a sequence of 3D images, named as Direct Bundle Adjustment (DBA). This algorithm simultaneously optimizes the global pose parameters of image frames and the intensity values of the fused global image using the 3D image data directly (without extracting features from the images). This one-step 3D image fusion approach is achieved by formulating... |
Offset-free Model Predictive Control: A Ball Catching Application with a Spherical Soft Robotic Arm | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636608/ | [
"Yaohui Huang",
"Matthias Hofer",
"Raffaello D’Andrea",
"Yaohui Huang",
"Matthias Hofer",
"Raffaello D’Andrea"
] | This paper presents an offset-free model predictive controller for fast and accurate control of a spherical soft robotic arm. In this control scheme, a linear model is combined with an online disturbance estimation technique to systematically compensate model deviations. Dynamic effects such as material relaxation resulting from the use of soft materials can be addressed to achieve offset-free tra... |
Embedded Hardware Appropriate Fast 3D Trajectory Optimization for Fixed Wing Aerial Vehicles by Leveraging Hidden Convex Structures | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636337/ | [
"Vivek Kantilal Adajania",
"Houman Masnavi",
"Fatemeh Rastgar",
"Karl Kruusamae",
"Arun Kumar Singh",
"Vivek Kantilal Adajania",
"Houman Masnavi",
"Fatemeh Rastgar",
"Karl Kruusamae",
"Arun Kumar Singh"
] | Most commercially available fixed-wing aerial vehicles (FWV) can carry only small, lightweight computing hardware such as Jetson TX2 onboard. Solving non-linear trajectory optimization on these computing resources is computationally challenging even while considering only the kinematic motion model. Most importantly, the computation time increases sharply as the environment becomes more cluttered.... |
Probabilistic Iterative LQR for Short Time Horizon MPC | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636295/ | [
"Teguh Santoso Lembono",
"Sylvain Calinon",
"Teguh Santoso Lembono",
"Sylvain Calinon"
] | Optimal control is often used in robotics for planning a trajectory to achieve some desired behavior, as expressed by the cost function. Most works in optimal control focus on finding a single optimal trajectory, which is then typically tracked by another controller. In this work, we instead consider trajectory distribution as the solution of an optimal control problem, resulting in better trackin... |
Efficient and Reactive Planning for High Speed Robot Air Hockey | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636263/ | [
"Puze Liu",
"Davide Tateo",
"Haitham Bou-Ammar",
"Jan Peters",
"Puze Liu",
"Davide Tateo",
"Haitham Bou-Ammar",
"Jan Peters"
] | Highly dynamic robotic tasks require high-speed and reactive robots. These tasks are particularly challenging due to the physical constraints, hardware limitations, and the high uncertainty of dynamics and sensor measures. To face these issues, it’s crucial to design robotics agents that generate precise and fast trajectories and react immediately to environmental changes. Air hockey is an example... |
Closed-Loop Robotic Cooking of Scrambled Eggs with a Salinity-based ‘Taste’ Sensor | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636750/ | [
"Grzegorz Sochacki",
"Josie Hughes",
"Simon Hauser",
"Fumiya Iida",
"Grzegorz Sochacki",
"Josie Hughes",
"Simon Hauser",
"Fumiya Iida"
] | The sense of taste is fundamental to a human chef’s ability to cook tasty food. To develop robots that can demonstrate human-like cooking, robots need to be equipped with a sense of taste and enabled to use this perception capability to improve or understand the food which they are cooking. We propose a first study of using a salinity sensor to provide a robot with a sense of saltiness. We then de... |
Car Racing Line Optimization with Genetic Algorithm using Approximate Homeomorphism | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636503/ | [
"Jaroslav Klapálek",
"Antonín Novák",
"Michal Sojka",
"Zdeněk Hanzálek",
"Jaroslav Klapálek",
"Antonín Novák",
"Michal Sojka",
"Zdeněk Hanzálek"
] | In every timed car race, the goal is to drive through the racing track as fast as possible. The total time depends on selection of the racing line. Following a better racing line often decides who wins. In this paper, we solve the optimal racing line problem using a genetic algorithm. We propose a novel racing line encoding based on a homeomorphic transformation called Matryoshka mapping. We evalu... |
Human Motion Imitation using Optimal Control with Time-Varying Weights | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636520/ | [
"Shouyo Ishida",
"Tatsuki Harada",
"Pamela Carreno-Medrano",
"Dana Kulić",
"Gentiane Venture",
"Shouyo Ishida",
"Tatsuki Harada",
"Pamela Carreno-Medrano",
"Dana Kulić",
"Gentiane Venture"
] | Research in biomechanics hypothesizes that human motion is optimal with respect to an unknown cost function that varies depending on the action and/or task. This unknown cost function is often approximated as the weighted sum of a set of features or basis cost functions. As a person performs a sequence of actions, the weights associated to each of these basis functions are likely to vary over time... |
Soft Robot Configuration Estimation and Control Using Simultaneous Localization and Mapping | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635896/ | [
"Christian Sorensen",
"Phillip Hyatt",
"Matthew Ricks",
"Seth Nielsen",
"Marc D. Killpack",
"Christian Sorensen",
"Phillip Hyatt",
"Matthew Ricks",
"Seth Nielsen",
"Marc D. Killpack"
] | In this paper we present a novel approach to accomplishing soft robot configuration estimation and control using RGB-D cameras and SLAM-based methods. By placing cameras on the unactuated sections of our large-scale (approximately 2 meters long) pneumatic soft robot, we can map an environment and then estimate the orientation of the robot links using landmark-based localization. Using the orientat... |
A Parameter Identification Method for Static Cosserat Rod Models: Application to Soft Material Actuators with Exteroceptive Sensors | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636447/ | [
"Max Bartholdt",
"Mats Wiese",
"Moritz Schappler",
"Svenja Spindeldreier",
"Annika Raatz",
"Max Bartholdt",
"Mats Wiese",
"Moritz Schappler",
"Svenja Spindeldreier",
"Annika Raatz"
] | Soft material robotics is a rather young research field in the robotics and material science communities. A popular design is the soft pneumatic actuator (SPA) which, if connected serially, becomes a highly compliant manipulator. This high compliance makes it possible to adapt to the environment and in the future might be very useful for manipulation tasks in narrow and wound environments. A centr... |
Analytical Modeling of a Soft Pneu-net Actuator Based on Finite Strain Beam Theory | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635996/ | [
"Sachin Sachin",
"Zhongkui Wang",
"Shinichi Hirai",
"Sachin Sachin",
"Zhongkui Wang",
"Shinichi Hirai"
] | In this paper, we propose a simple analytical model for pneu-net soft actuator. The model is based on Euler– Bernoulli finite strain hyperelastic thin cantilever beam theory. The deformation of the air chambers is modelled using infinitesimal strain membrane theory. The proposed theoretical model estimates the deformation and force characteristics of the actuator. The developed model accounts the ... |
Soft-CCD Algorithm for Inverse Kinematics of Soft Continuum Manipulators | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635921/ | [
"Zhiyuan Zhang",
"Songtao Wang",
"Deshan Meng",
"Xueqian Wang",
"Bin Liang",
"Zhiyuan Zhang",
"Songtao Wang",
"Deshan Meng",
"Xueqian Wang",
"Bin Liang"
] | To date, soft robots have been increasingly designed and analyzed, especially, Soft Continuum Manipulators (SCMs). Due to dexterous deformability, their Inverse Kinematics (IK) is still difficult to solve. Cyclic Coordinate Descent (CCD) algorithm is one of the classical optimization algorithms to solve IK of rigid manipulators with prismatic or rotational joints. However, it cannot be directly ex... |
Shape-centric Modeling for Soft Robot Inchworm Locomotion | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636695/ | [
"Alexander H. Chang",
"Caitlin Freeman",
"Arun Niddish Mahendran",
"Vishesh Vikas",
"Patricio A. Vela",
"Alexander H. Chang",
"Caitlin Freeman",
"Arun Niddish Mahendran",
"Vishesh Vikas",
"Patricio A. Vela"
] | Soft robot modeling tends to prioritize soft robot dynamics in order to recover how they might behave. Soft robot design tends to focus on how to use compliant elements with actuation to effect certain canonical movement profiles. For soft robot locomotors, these profiles should lead to locomotion. Naturally, there is a gap between the emphasis of computational modeling and the needs of locomotion... |
SoPrA: Fabrication & Dynamical Modeling of a Scalable Soft Continuum Robotic Arm with Integrated Proprioceptive Sensing | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636539/ | [
"Yasunori Toshimitsu",
"Ki Wan Wong",
"Thomas Buchner",
"Robert Katzschmann",
"Yasunori Toshimitsu",
"Ki Wan Wong",
"Thomas Buchner",
"Robert Katzschmann"
] | Due to their inherent compliance, soft robots are more versatile than rigid linked robots when they interact with their environment, such as object manipulation or biomimetic motion, and are considered to be the key element in introducing robots to everyday environments. Although various soft robotic actuators exist, past research has focused primarily on designing and analyzing single components.... |
Dynamic modelling and visco-elastic parameter identification of a fibre-reinforced soft fluidic elastomer manipulator | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636785/ | [
"Azadeh Shariati",
"Jialei Shi",
"Sarah Spurgeon",
"Helge A Wurdemann",
"Azadeh Shariati",
"Jialei Shi",
"Sarah Spurgeon",
"Helge A Wurdemann"
] | A dynamic model of a soft fibre-reinforced fluidic elastomer is presented and experimentally verified, which can be used for model-based controller design. Due to the inherent visco-(hyper)elastic characteristics and nonlinear time-dependent behaviour of soft fluidic elastomer robots, analytic dynamic modelling is challenging. The fibre reinforced noninflatable soft fluidic elastomer robot used in... |
Casting manipulation of unknown string by robot arm | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635837/ | [
"Kenta Tabata",
"Hiroaki Seki",
"Tokuo Tsuji",
"Tatsuhiro Hiramitsu",
"Kenta Tabata",
"Hiroaki Seki",
"Tokuo Tsuji",
"Tatsuhiro Hiramitsu"
] | Casting manipulation has been studied to expand the robot’s movable range. In this manipulation, the robot throws and reaches the end effector to a distant target. Usually, a special casting manipulator, which consists of rigid arm links and specific flexible linear objects, is constructed for an effective casting manipulation. However, the special manipulator cannot perform normal manipulations, ... |
Deformation Control of a Deformable Object Based on Visual and Tactile Feedback | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636157/ | [
"Yuhao Guo",
"Xin Jiang",
"Yunhui Liu",
"Yuhao Guo",
"Xin Jiang",
"Yunhui Liu"
] | In this paper, we presented a new method for deformation control of deformable objects, which utilizes both visual and tactile feedback. At present, manipulation of deformable objects is basically formulated by assuming positional constraints. But in fact, in many situations manipulation has to be performed under actively applied force constraints. This scenario is considered in this research. In ... |
Real-Time Safety and Control of Robotic Manipulators with Torque Saturation in Operational Space | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636794/ | [
"Muhammad Ali Murtaza",
"Sergio Aguilera",
"Vahid Azimi",
"Seth Hutchinson",
"Muhammad Ali Murtaza",
"Sergio Aguilera",
"Vahid Azimi",
"Seth Hutchinson"
] | This paper presents a real-time safety and control for robot manipulators using control barrier functions and control Lyapunov functions in operational space. We first define the operational space in terms of system dynamics, jacobian, and torques and then ensure safety by designing Control Barrier Functions (CBF) around the body links of the robotic manipulator. The control barrier function provi... |
Robot Hand based on a Spherical Parallel Mechanism for Within-Hand Rotations about a Fixed Point | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636704/ | [
"Vatsal V. Patel",
"Aaron M. Dollar",
"Vatsal V. Patel",
"Aaron M. Dollar"
] | Rotating a grasped object about all three spatial axes is challenging, because kinematically redundant robot hands require complex control schemes for within-hand rotations, and simple parallel grippers require inefficient whole arm motions. We present a novel 3-finger robot hand design inspired by a spherical parallel mechanism that achieves these rotations with just 3 actuators. The hand is desi... |
Learning compliant grasping and manipulation by teleoperation with adaptive force control | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636832/ | [
"Chao Zeng",
"Shuang Li",
"Yiming Jiang",
"Qiang Li",
"Zhaopeng Chen",
"Chenguang Yang",
"Jianwei Zhang",
"Chao Zeng",
"Shuang Li",
"Yiming Jiang",
"Qiang Li",
"Zhaopeng Chen",
"Chenguang Yang",
"Jianwei Zhang"
] | In this work, we focus on improving the robot’s dexterous capability by exploiting visual sensing and adaptive force control. TeachNet, a vision-based teleoperation learning framework, is exploited to map human hand postures to a multi-fingered robot hand. We augment TeachNet, which is originally based on an imprecise kinematic mapping and position-only servoing, with a biomimetic learning-based c... |
Dynamic-based RCM Torque Controller for Robotic-Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636823/ | [
"Marco Minelli",
"Cristian Secchi",
"Marco Minelli",
"Cristian Secchi"
] | In this paper we propose a novel flexible and optimization-free controller for standard torque-controlled manipulator for Robotic-Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery. A novel method has been developed to model the constraint introduced by the laparoscopic tool, i.e. the remote center of motion, exploiting closed chain manipulators theory, and the final controller was synthesized considering the ef... |
A Novel Wax Based Piezo Actuator for Autonomous Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty (Piezo-DALK) | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636153/ | [
"J. D. Opfermann",
"M. Barbic",
"M. Khrenov",
"S. Guo",
"N. R. Sarfaraz",
"J. U. Kang",
"A. Krieger",
"J. D. Opfermann",
"M. Barbic",
"M. Khrenov",
"S. Guo",
"N. R. Sarfaraz",
"J. U. Kang",
"A. Krieger"
] | This paper reports the design and evaluation of a novel piezo based actuator for needle drive in autonomous Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty (piezo-DALK). The actuator weighs less than 8g and is 20mm x 20mm x 10.5mm in size, making it ideal for eye-mounted applications. Mean open loop positional deviation was 1.17 ± 3.15um, and system repeatability and accuracy were 17.16um and 18.33um, respect... |
A Wearable Robotic Device for Assistive Navigation and Object Manipulation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636126/ | [
"Lingqiu Jin",
"He Zhang",
"Cang Ye",
"Lingqiu Jin",
"He Zhang",
"Cang Ye"
] | This paper presents a hand-worn assistive device to assist a visually impaired person with object manipulation. The device uses a Google Pixel 3 as the computational platform, a Structure Core (SC) sensor for perception, a speech interface, and a haptic interface for human-device interaction. W-ROMA is intended to assist a visually impaired person to locate a target object (nearby or afar) and gui... |
Capturing Skill State in Curriculum Learning for Human Skill Acquisition | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636850/ | [
"Keya Ghonasgi",
"Reuth Mirsky",
"Sanmit Narvekar",
"Bharath Masetty",
"Adrian M. Haith",
"Peter Stone",
"Ashish D. Deshpande",
"Keya Ghonasgi",
"Reuth Mirsky",
"Sanmit Narvekar",
"Bharath Masetty",
"Adrian M. Haith",
"Peter Stone",
"Ashish D. Deshpande"
] | Humans learn complex motor skills with practice and training. Though the learning process is not fully understood, several theories from motor learning, neuroscience, education, and game design suggest that curriculum-based training may be the key to efficient skill acquisition. However, designing such a curriculum and understanding its effects on learning are challenging problems. In this paper, ... |
Online Verification of Impact-Force-Limiting Control for Physical Human-Robot Interaction | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636610/ | [
"Stefan B. Liu",
"Matthias Althoff",
"Stefan B. Liu",
"Matthias Althoff"
] | Humans must remain unharmed during their interaction with robots. We present a new method guaranteeing impact force limits when humans and robots share a workspace. Formal guarantees are realized using an online verification method, which plans and verifies fail-safe maneuvers through predicting reachable impact forces by considering all future possible scenarios. We model collisions as a coupled ... |
Dual-Filtering for On-Line Simultaneously Estimate Weights and Phase Parameter of Probabilistic Movement Primitives for Human-Robot Collaboration | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636654/ | [
"Ren.C Luo",
"Licong Mai",
"Ren.C Luo",
"Licong Mai"
] | The Probabilistic Movement Primitives (ProMPs) is an essential issue and framework for robotics Learning from Demonstration (LfD). It has been successfully applied to the robotics field in tasks such as skill acquisition and Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC). In this paper, we focus on its adaptability in the HRC scenario, in which the adaptability of the ProMPs allows the robot to predict the futur... |
Sampling-based Inverse Reinforcement Learning Algorithms with Safety Constraints | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636672/ | [
"Johannes Fischer",
"Christoph Eyberg",
"Moritz Werling",
"Martin Lauer",
"Johannes Fischer",
"Christoph Eyberg",
"Moritz Werling",
"Martin Lauer"
] | Planning for robotic systems is frequently formulated as an optimization problem. Instead of manually tweaking the parameters of the cost function, they can be learned from human demonstrations by Inverse Reinforcement Learning (IRL). Common IRL approaches employ a maximum entropy trajectory distribution that can be learned with soft reinforcement learning, where the reward maximization is regular... |
Radar Based Target Tracking and Classification for Efficient Robot Speed Control in Fenceless Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636170/ | [
"Barnaba Ubezio",
"Christian Schöffmann",
"Lucas Wohlhart",
"Stephan Mülbacher-Karrer",
"Hubert Zangl",
"Michael Hofbaur",
"Barnaba Ubezio",
"Christian Schöffmann",
"Lucas Wohlhart",
"Stephan Mülbacher-Karrer",
"Hubert Zangl",
"Michael Hofbaur"
] | Awareness of its surroundings is a crucial capability for a robot meant to be working alongside other robots or human operators. When considering safety norms and modalities, in particular the Speed and Separation Monitoring (SSM), proper proximity information can make the difference in the overall efficiency of a use case, for example avoiding unnecessary penalizations in the cycle-time. This pap... |
"Safe Skin" - A Low-Cost Capacitive Proximity-Force-Fusion Sensor for Safety in Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636308/ | [
"Zhen Wang",
"Heyang Gao",
"Alexander Schmitz",
"Sophon Somlor",
"Tito Pradhono Tomo",
"Shigeki Sugano",
"Zhen Wang",
"Heyang Gao",
"Alexander Schmitz",
"Sophon Somlor",
"Tito Pradhono Tomo",
"Shigeki Sugano"
] | This paper presents the design and evaluation of the low-cost capacitive proximity-force-fusion sensor "safe skin", which can measure simultaneously the proximity of humans as well as the contact force. It was designed such that the force and proximity sensing functions can work concurrently without interfering with each other. Moreover, active shielding, on-chip digitization and ground isolation ... |
Text-based robot emotion and human-like emotional transition | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636793/ | [
"Yu-Jung Chae",
"Tae-Hee Jeon",
"ChangHwan Kim",
"Sung-Kee Park",
"Yu-Jung Chae",
"Tae-Hee Jeon",
"ChangHwan Kim",
"Sung-Kee Park"
] | Studies on the production of emotions have been conducted to create robotic facial expressions. The reported methodologies for generating emotions for a robot have focused on recognizing a user’s emotions using devices, such as cameras and microphones, and then generating the reactive emotions of a robot according to the user’s emotions. However, these methodologies may have some limitations in de... |
Personalization of Human-Robot Gestural Communication through Voice Interaction Grounding | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636105/ | [
"Heike Brock",
"Randy Gomez",
"Heike Brock",
"Randy Gomez"
] | In this paper we develop a gestural communication perception system for a social robot companion that is able to autonomously learn novel gestures on-the-fly. The system constantly tracks human gestural activities with a camera and evaluates the performed gestures under an open-set assumption. This allows for the identification of unknown gestures. Once detected, the system stores motion sequences... |
"Pretending to be Okay in a Sad Voice": Social Robot’s Usage of Verbal and Nonverbal Cue Combination and its Effect on Human Empathy and Behavior Inducement | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636709/ | [
"Byeong June Moon",
"JongSuk Choi",
"Sonya S. Kwak",
"Byeong June Moon",
"JongSuk Choi",
"Sonya S. Kwak"
] | Inducing a user’s behavior through social interaction is a goal that a social robot aims to achieve. It has been argued that empathy has a strong effect on behavior inducement. In human-human interaction, it has been verified that the influence of a nonverbal cue on empathy outweighs that of a verbal cue when those are used in a combined way. The objectives of this study are to explore if such out... |
Pain Expression-based Visual Feedback Method for Care Training Assistant Robot with Musculoskeletal Symptoms | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636671/ | [
"Miran Lee",
"Dinh Tuan Tran",
"Joo-Ho Lee",
"Miran Lee",
"Dinh Tuan Tran",
"Joo-Ho Lee"
] | A human patient simulator (HPS) can achieve effective visual-, auditory-, text-, and alarm-based feedback methods in care or nursing education. Among these, the method of visual feedback is important to design an HPS that can express emotions or feelings of pain like an actual human does because this method allows an immediate reaction between robots and humans. This study aims to develop an avata... |
Tachyon: Design and Control of High Payload, Robust, and Dynamic Quadruped Robot with Series-Parallel Elastic Actuators | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636196/ | [
"Yasuhisa Kamikawa",
"Masaya Kinoshita",
"Noriaki Takasugi",
"Katsufumi Sugimoto",
"Toshimitsu Kai",
"Takashi Kito",
"Atsushi Sakamoto",
"Kenichiro Nagasaka",
"Yasunori Kawanami",
"Yasuhisa Kamikawa",
"Masaya Kinoshita",
"Noriaki Takasugi",
"Katsufumi Sugimoto",
"Toshimitsu Kai",
"Takashi Kito",
"Atsushi Sakamoto",
"Kenichiro Nagasaka",
"Yasunori Kawanami"
] | This paper introduces a quadruped robot, Tachyon, which aims to achieve high payload, robust, and dynamic locomotion on the various terrain with high energy efficiency. Thanks to a novel compact series-parallel elastic actuator (SPEA) on the upper link and a four-bar linkage design in the knee joint for constant vertical foot force, the 41-kg robot can carry more than 20 kg of payloads with dynami... |
Modeling and Trajectory Optimization for Standing Long Jumping of a Quadruped with A Preloaded Elastic Prismatic Spine | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636606/ | [
"Keran Ye",
"Konstantinos Karydis",
"Keran Ye",
"Konstantinos Karydis"
] | This paper presents a novel methodology to model and optimize trajectories of a quadrupedal robot with spinal compliance to improve standing jump performance compared to quadrupeds with a rigid spine. We introduce an elastic model for a prismatic robotic spine that is actively preloaded and mechanically lock-enabled at initial and maximum length, and develop a constrained trajectory optimization m... |
The Usage of Kinematic Singularities to Produce Periodic High-Powered Locomotion | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636062/ | [
"Chang Liu",
"Mark Plecnik",
"Chang Liu",
"Mark Plecnik"
] | Legged robots primarily energize their center of mass through external contact during stance phase. This links their range of possible motions to actuator power limits applied during usually short periods of time. Enabling limb actuators to pump energy into the system during non-contact phases can greatly extend the energetic profile of possible motions. However, funneling this extra energy into u... |
Quadrupedal template model for parametric stability analysis of trotting gaits | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9635974/ | [
"Lorenzo Boffa",
"Anna Sesselmann",
"Máximo A. Roa",
"Lorenzo Boffa",
"Anna Sesselmann",
"Máximo A. Roa"
] | Simple template models have proven useful for understanding the underlying dynamics of legged locomotion. The most common one, the SLIP model, considers the legs as linear springs with constant stiffness, and it explains well the radial dynamics of the legs. However, in order to study the influence of the leg swing dynamics and leg segmentation on gait stability, more complex models are required. ... |
Coupling-dependent convergence behavior of phase oscillators with tegotae-control | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636646/ | [
"Simon Hauser",
"Matthieu Dujany",
"Jonathan Arreguit",
"Auke Ijspeert",
"Fumiya Iida",
"Simon Hauser",
"Matthieu Dujany",
"Jonathan Arreguit",
"Auke Ijspeert",
"Fumiya Iida"
] | A bio-inspired way to model locomotion is using a network of coupled phase oscillators to create a Central Pattern Generator (CPG). The recently developed feedback control method tegotae includes exteroceptive force feedback into the governing phase update equations, leading to gait limit cycles. However, the oscillator coupling weights are often determined empirically. Here, we first investigate ... |
Towards autonomous area inspection with a bio-inspired underwater legged robot | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636316/ | [
"Giacomo Picardi",
"Rossana Lovecchio",
"Marcello Calisti",
"Giacomo Picardi",
"Rossana Lovecchio",
"Marcello Calisti"
] | Recently, a new category of bio-inspired legged robots moving directly on the seabed have been proposed to complement the abilities of traditional underwater vehicles and to enhance manipulation and sampling tasks. So far, only tele-operated use of underwater legged robots has been reported and in this paper we attempt to fill such gap by presenting the first step towards autonomous area inspectio... |
Imagination-enabled Robot Perception | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636359/ | [
"Patrick Mania",
"Franklin Kenghagho Kenfack",
"Michael Neumann",
"Michael Beetz",
"Patrick Mania",
"Franklin Kenghagho Kenfack",
"Michael Neumann",
"Michael Beetz"
] | Many of today’s robot perception systems aim at accomplishing perception tasks that are too simplistic and too hard. They are too simplistic because they do not require the perception systems to provide all the information needed to accomplish manipulation tasks. Typically the perception results do not include information about the part structure of objects, articulation mechanisms and other attri... |
IROS 2021 Accepted Paper Meta Info Dataset
This dataset is collect from the IROS 2021-2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/conhome/9981026/proceeding) as well as the arxiv website DeepNLP paper arxiv (http://www.deepnlp.org/content/paper/iros2021). For researchers who are interested in doing analysis of IROS 2021 accepted papers and potential trends, you can use the already cleaned up json files. Each row contains the meta information of a paper in the IROS 2021 conference. To explore more AI & Robotic papers (NIPS/ICML/ICLR/IROS/ICRA/etc) and AI equations, feel free to navigate the Equation Search Engine (http://www.deepnlp.org/search/equation) as well as the AI Agent Search Engine to find the deployed AI Apps and Agents (http://www.deepnlp.org/search/agent) in your domain.
Equations Latex code and Papers Search Engine
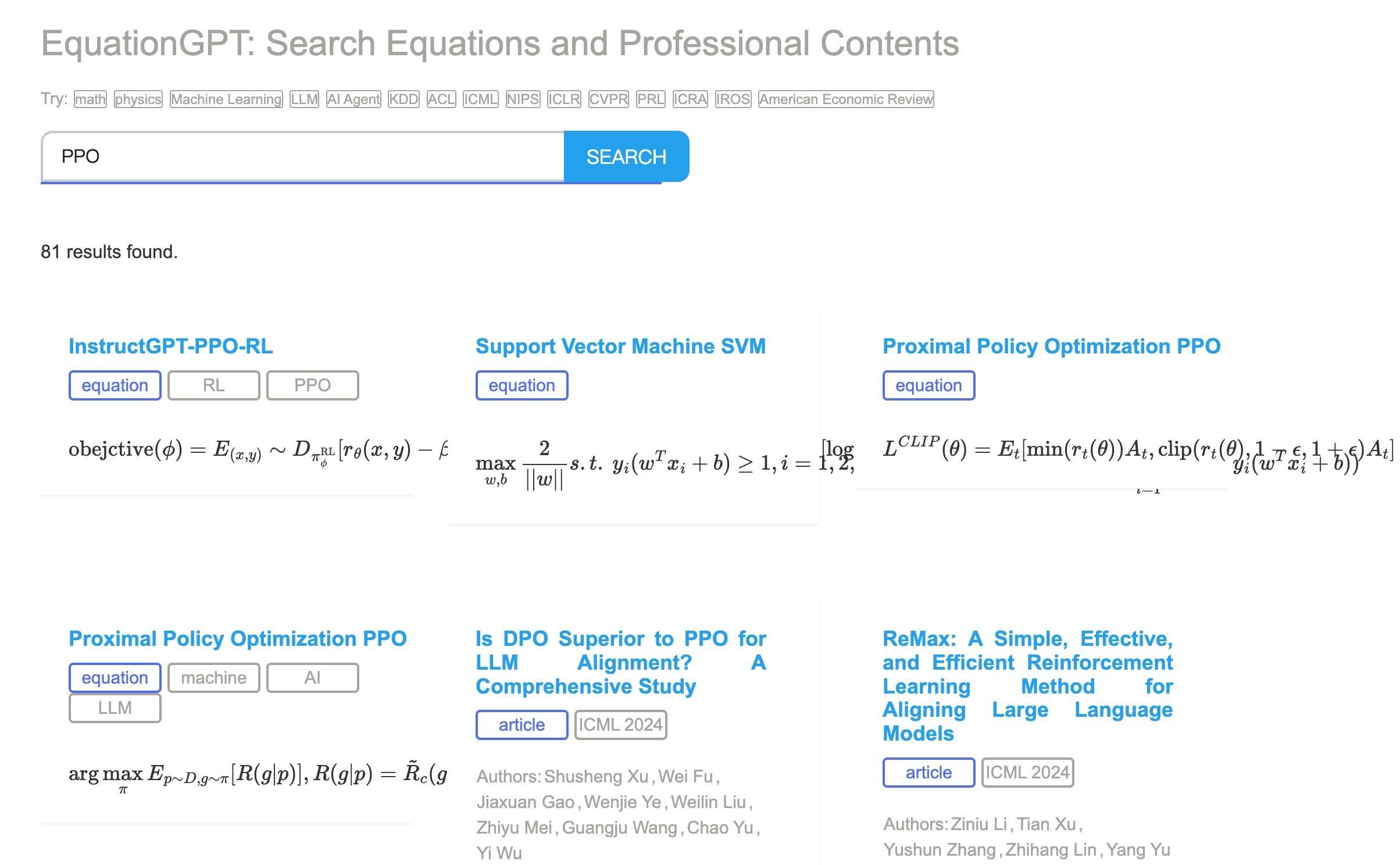
Meta Information of Json File of Paper
{
"title": "Learning-based Localizability Estimation for Robust LiDAR Localization",
"detail_url": "https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9982257/",
"author_list": ["Julian Nubert", "Etienne Walther", "Shehryar Khattak", "Marco Hutter", "Julian Nubert", "Etienne Walther", "Shehryar Khattak", "Marco Hutter"],
"abstract": "LiDAR-based localization and mapping is one of the core components in many modern robotic systems due to the direct integration of range and geometry, allowing for precise motion estimation and generation of high quality maps in real-time. Yet, as a consequence of insufficient environmental constraints present in the scene, this dependence on geometry can result in localization failure, happening ..."
}
Related
AI Agent Marketplace and Search
AI Agent Marketplace and Search
Robot Search
Equation and Academic search
AI & Robot Comprehensive Search
AI & Robot Question
AI & Robot Community
AI Agent Marketplace Blog
AI Agent Reviews
AI Agent Marketplace Directory
Microsoft AI Agents Reviews
Claude AI Agents Reviews
OpenAI AI Agents Reviews
Saleforce AI Agents Reviews
AI Agent Builder Reviews
AI Equation
List of AI Equations and Latex
List of Math Equations and Latex
List of Physics Equations and Latex
List of Statistics Equations and Latex
List of Machine Learning Equations and Latex
- Downloads last month
- 30